- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion halts prepregnancy DR progression: Study
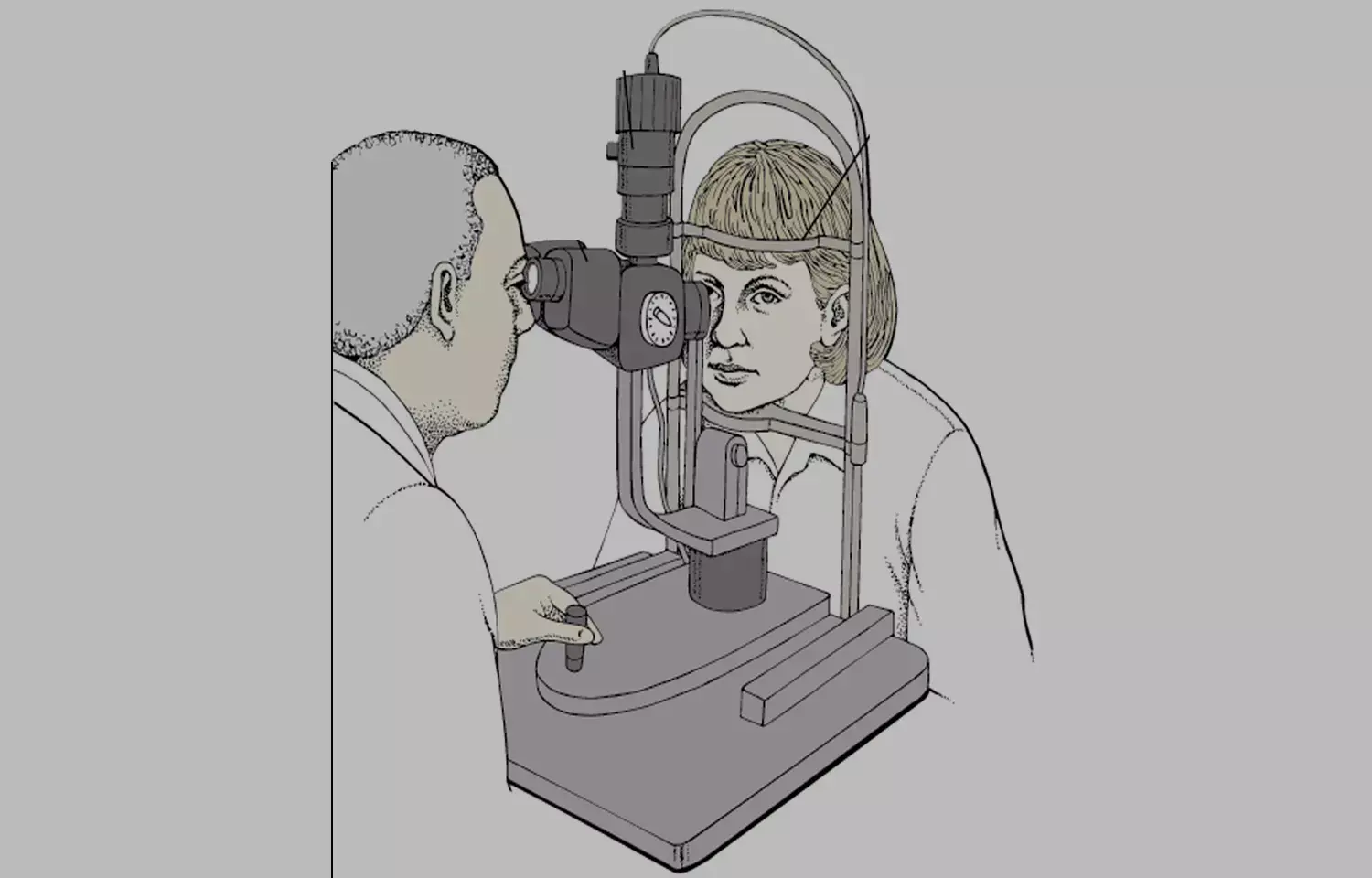
France: Women having prepregnancy diabetic retinopathy (DR) treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) during and before pregnancy had a lower risk of DR progression, according to a recent study in the journal Diabetes Care.
The researchers suggests that women with type 1 diabetes should undergo ophthalmologic examination both before and during pregnancy. Women having severe prepregnancy diabetic retinopathy should be treated before planning pregnancy.
Pregnancy is associated with DR development and progression but DR incidence remains unclear. Julien Bourry, Lille University Hospital, Lille, France, and colleagues assessed the rate of DR progression and its predictors during pregnancies in type 1 diabetes patients.
The researchers reported the retrospective data from pregnancies in patients with type 1 diabetes followed in Lille, France (1997–2015). In cases of severe nonproliferative retinopathy or progression, eye examination was performed every 3 months or every month.
Progression was defined by DR degradation (≥1 stage of the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study [ETDRS] classification); it included DR development and worsening in patients without and with prepregnancy DR, respectively.
The study included a total of 499 pregnancies in 375 patients; prepregnancy retinopathy was present in 30.3%.
Key findings of the study include:
- Progression, development, and worsening rates were 21.8%, 24.4% of those without retinopathy, and 15.9% of those with retinopathy, respectively.
- Development of sight-threatening retinopathy was rare. Progression mainly occurred in early or midpregnancy.
- Elevated prepregnancy HbA1c and duration of diabetes ≥10 years were predictors of DR progression. Among pregnancies with prepregnancy DR, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) tended to decrease the risk of DR progression.
- Among CSII-treated patients, those with prepregnancy DR had a significantly decreased risk of DR progression.
- Among the 270 pregnancies of women with any DR during pregnancy who returned for a postpartum ophthalmologic examination, the rate of progression was only 4.1% and the rate of regression was 9.3%.
"This study provides epidemiologic data on progression of retinopathy during pregnancy and will be useful for future guidelines for retinopathy screening," wrote the authors.
The study titled, "Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy and Predictors of Its Development and Progression During Pregnancy in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Report of 499 Pregnancies," is published in the journal Diabetes Care.
DOI: https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/44/1/181
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


