- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Daily usage of high insulin dose tied to cancer risk in type 1 diabetes: JAMA
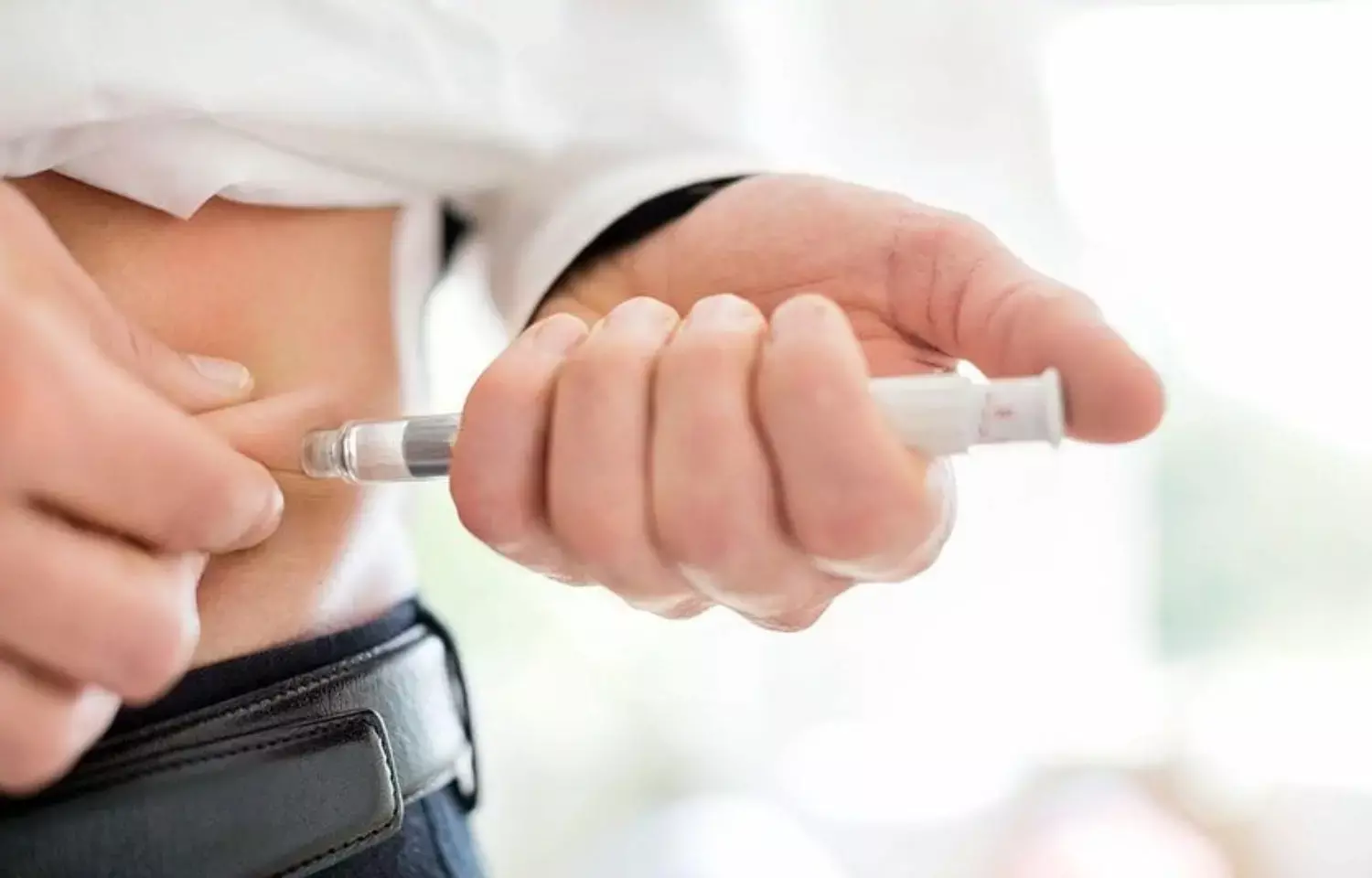
Pennsylvania: There is a dose-dependent association between insulin and cancer incidence risk among type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients, states new study results published in the JAMA Oncology.
Diabetes and cancer are common diseases having a tremendous impact on health worldwide. Epidemiologic evidence suggests that people with diabetes are at significantly higher risk for many forms of cancer. In type 1 diabetes(T1D), the body cannot produce the hormone insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. T1D patients are treated with insulin to survive. Insulin is known to increase cell production and reduces cell death, so there are chances that something may go wrong and cancer may develop. Previous studies have found a higher incidence of certain cancers in T1D compared with the general population. However, no studies have evaluated the risk factors of cancer incidence in T1D.
Zhong W, Merck Research Labs, Merck & Co Inc, Pennsylvania, and her team conducted a study to explore the associations of risk factors with cancer incidence in patients with T1D over a 28-year follow-up period.
Investigators used data from Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) and the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study and included 1303 patients who volunteered to continue in the EDIC follow-up study. Cancer incidence was calculated and associations of risk factors with cancer incidence were evaluated using Cox proportional hazards regression models. As daily insulin dose (time-dependent variable) remained significant in the multivariable model, it was also examined as a fixed variable (mean dose during follow-up). Investigators examined cancer incidence by 3 categories of mean daily insulin dose: low (<0.5 units/kg), medium (≥0.5 and <0.8 units/kg), and high (≥0.8 units/kg).
Key findings of the study,
• Of the total,7% had cancer diagnoses after a total of 33 813 person-years follow-up, and the incidence rate was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.2-3.3) per 1000 person-years.
• 9% developed cancer within 10 years, 33% developed cancer between 11 and 20 years, and 58% developed cancer between 21 and 28 years.
• Age and sex were associated with cancer incidence, for age (HR-1.08 ); for female sex(HR-1.74)
• Exercising habits and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were inversely associated and daily insulin dose was associated with cancer incidence after adjusting for age and sex.
• Daily insulin dose remained associated with cancer incidence in the multivariable model 1 (HR-5.93) and model 2 (HR-4.13)
• Cancer incidence was 2.11, 2.87, and 2.91 per 1000 person-years in the low-, medium-, and high-dose groups, respectively.
The authors conclude that daily insulin dose is associated with cancer risk in T1D. The study showed that the HRs were significantly higher in the high-dose vs low-dose group, suggesting those using higher daily doses of insulin had a more than 4-fold increase in the risk of a cancer diagnosis. In the future, larger studies in T1D are needed to validate this association.
Reference:
Zhong W, Mao Y. Daily Insulin Dose and Cancer Risk Among Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. JAMA Oncol. Published online July 28, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.2960
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


