- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Presence of high-level VCAM-1 tied to severity of diabetic retinopathy: Study
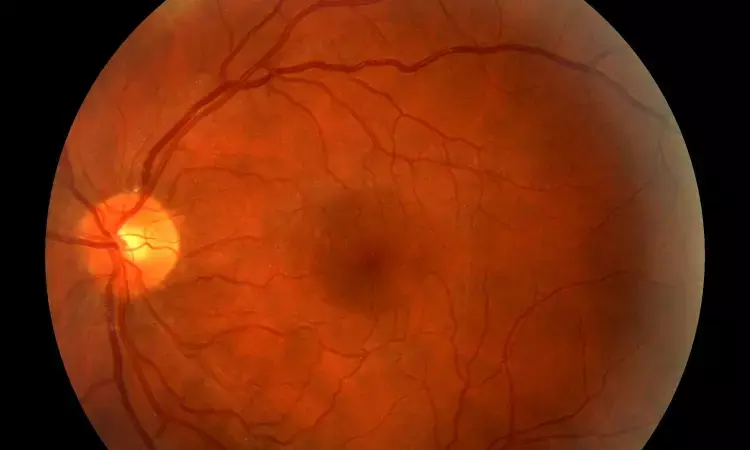
China: A recent study published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications has shown the presence of a high level of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) related to the severity of DR.
Based on the above findings, Yinglei Xu, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Shandong, China, and colleagues concluded that VCAM-1 is a potential detection biomarker for diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy, one of the common microvascular complications of diabetes, is the most common cause of blindness and visual impairment worldwide. The global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is reported to be 27%. Diabetic retinopathy is an inflammatory disease comprising adhesion molecules. VCAM-1 is an adhesion molecule involved in tumour growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis processes. However, there needs to be more clarity on the exact role of VCAM-1 in DR, and there is a shortage of meta-analyses.
To fill the knowledge gap, the research team aimed to clarify the relationship between VCAM-1 and diabetic retinopathy and provide an experimental basis for further developing new treatment strategies targeting VCAM-1.
For this purpose, the researchers screened the role of VCAM-1 in DR by database searching. A systematic retrieval was performed for studies reporting the relationship between VCAM-1 and DR. A total of 932 relevant articles were retrieved through a systematic search. Twenty studies comprising 1881 participants (684 healthy controls and 463 DR patients) were included for full-text examination.
The study led to the following findings:
- In the DR group, the VCAM-1 increased significantly compared with the control group (SMD: 0.67).
- VCAM-1 level correlated with sample size, DR type, method, and severity based on subgroup analysis.
"A high level of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is present in patients with diabetic retinopathy and is related to the DR severity. Therefore, VCAM-1 is a potential detection biomarker for DR," the researchers wrote.
Reference:
The study titled "The role of VCAM-1 in diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis" was published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108380
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


