- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
RYGB better than Sleeve Gastrectomy to reduce CVD events in Type 2 Diabetes: Study
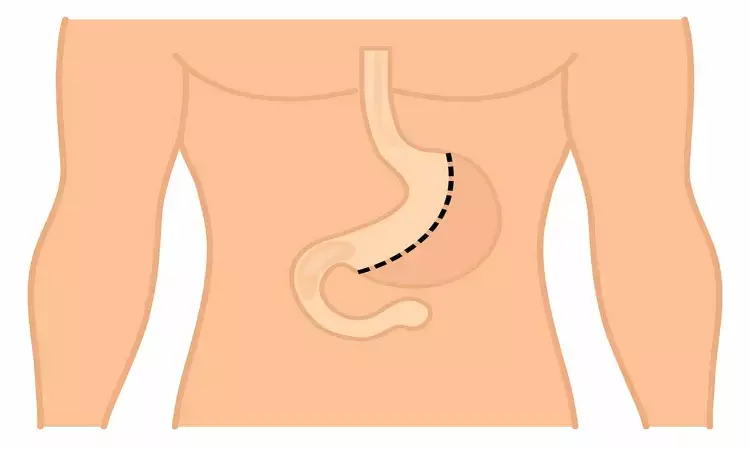
Metabolic surgery is popularly used to treat Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) that fails to respond to lifestyle and medication changes, rather than obesity.
Type 2 diabetes is associated with serious cardiovascular (CV) events. A new study by Dr Ali Aminian MD and team has found that Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) was much effective than Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) in controlling type 2 diabetes and obesity and reducing CV events . The study is published in Diabetes Care journal.
The objective of the study was to evaluate which one of the two most common metabolic surgical procedures is associated with greater reduction in risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity.
The study included a total of 13,490 patients including 1,362 RYGB, 693 sleeve gastrectomy SG, and 11,435 matched nonsurgical patients with T2DM and obesity who received their care at the Cleveland Clinic (1998–2017) were analyzed, with follow-up through December 2018. With multivariable Cox regression analysis we estimated time to incident extended MACE, defined as first occurrence of coronary artery events, Cerebrovascular events, heart failure, nephropathy, atrial fibrillation, and all-cause mortality.
The results of the study were found to be
• The cumulative incidence of the primary end point at 5 years was found to be 13.7% (95% CI 11.4–15.9) in the RYGB groups and 24.7% (95% CI 19.0–30.0) in the SG group, with an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 0.77 (95% CI 0.60–0.98, P = 0.04).
• Out of the six individual end points, RYGB was found to be associated with a significantly lower cumulative incidence of nephropathy at 5 years compared with SG (2.8% vs. 8.3%, respectively; HR 0.47 [95% CI 0.28–0.79], P = 0.005).
• Furthermore, RYGB was associated with a greater reduction in body weight, glycated hemoglobin, and use of medications to treat diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
• Five years after RYGB, patients required more upper endoscopy (45.8% vs. 35.6%, P < 0.001) and abdominal surgical procedures (10.8% vs. 5.4%, P = 0.001) compared with SG.
Dr Aminian and team concluded that "In patients with obesity and T2DM, RYGB may be associated with greater weight loss, better diabetes control, and lower risk of MACE and nephropathy compared with SG."
For further information: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-3023
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


