- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Subcutaneous injection of oxytocin can reduce perception of heat pain, claims study
Rabies
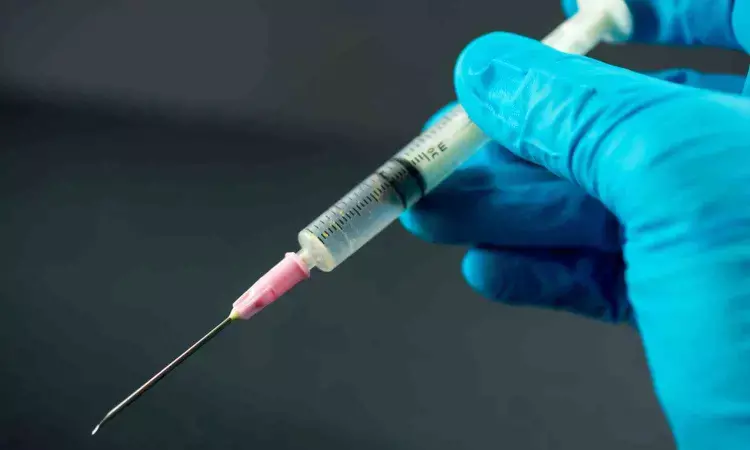
A recent clinical trial provided strong evidence that subcutaneous injections of oxytocin which is often often associated with social bonding, to hold the key to manage certain types of pain locally without the risk of addiction associated with many pain medications. This study opens up avenues to treat pain in a targeted manner, specifically heat-related pain, without affecting sensitivity to other types of pain or altering the overall threshold for pain perception.
This randomized-controlled trial explored the localized effects of oxytocin on pain management. The trial involved 18 healthy adult participants who underwent two separate sessions where they received either a subcutaneous injection of synthetic oxytocin (4mcg/2ml) or a saline placebo in a double-blind setup.
The results revealed that participants reported a significant reduction in the intensity and unpleasantness of heat pain on the arm that received the oxytocin injection, as measured 10 minutes post-injection with a thermode. This effect was localized, with no comparable pain reduction observed in the contralateral arm, which confirms the action of oxytocin to be restricted around the area of injection site. The hormone did not significantly affect the perception of mechanical or pressure pain, and it did not alter the thresholds for heat pain perception.
These findings highlight the unique potential of oxytocin as a localized treatment for acute heat pain by distinguishing it from other pain relievers that typically have a systemic effect. The specificity of pain-reducing effects by oxytocin could prove beneficial in medical scenarios where managing localized pain effectively and safely is crucial, such as in post-surgical recovery or treatment of localized inflammatory conditions.
The implications of this study are significant for both the scientific community and clinical practice. It suggests that oxytocin could be a potential alternative to traditional pain management therapies that offers a non-addictive and targeted approach to pain relief. The outcomes are optimistic about the potential of oxytocin to be developed into a treatment for localized pain conditions that anticipates further research to explore its mechanisms and broader applications.
With its well-known role in social bonding and its emerging capabilities in pain reduction, oxytocin may soon become a major player in the field of pain management and therapy. Further studies are imperative to explore additional therapeutic applications of oxytocin in pain management by paving the way for innovative treatments that harness the unique properties of the hormone.
Source:
Albinni, B., Zimmerman, M., Ross, J., Ozdoyuran, L., Alasha, V., Schuster, N. M., Said, E., & Case, L. (2024). Subcutaneous Oxytocin Injection Reduces Heat Pain: A randomized-controlled trial. In The Journal of Pain (p. 104547). Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2024.104547
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


