- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Type 2 Diabetes Raises Mortality but Not Reoperation After Hip and Knee Replacement: Study
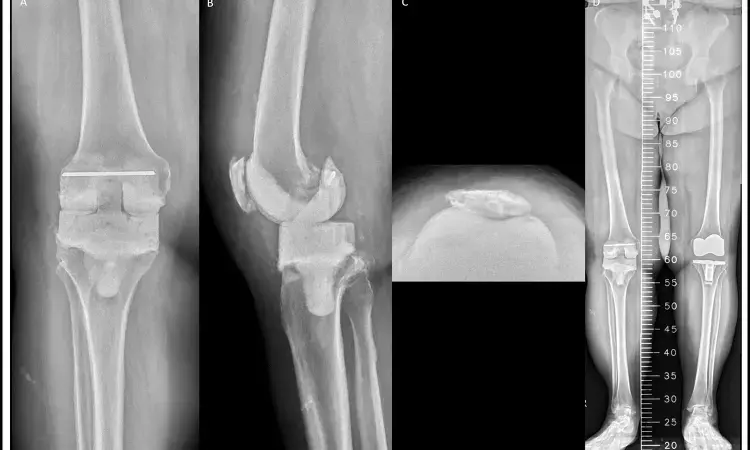
A large register-based study published in BMJ Open has reported that patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery face a higher risk of long-term mortality but not an increased risk of reoperation. The research analyzed outcomes from more than 190,000 procedures recorded in Swedish national registers, making it one of the most comprehensive evaluations of diabetes and joint replacement to date.
The authors note that while joint replacement is generally effective for improving quality of life in individuals with severe arthritis, the presence of chronic conditions such as diabetes may alter long-term outcomes.
According to the study, type 2 diabetes was linked to a greater likelihood of death after both hip and knee replacement, while the risk of requiring additional surgery remained unchanged compared to patients without diabetes. Short-term adverse events, such as complications occurring soon after surgery, were only minimally affected.
The researchers emphasize that other factors—including body mass index and the presence of additional health conditions—were more strongly associated with the need for reoperation and also influenced mortality risk. This suggests that while diabetes itself contributes to poorer survival, the interplay of obesity and comorbid illnesses may be equally or more important in determining surgical outcomes.
The authors conclude that careful preoperative assessment and long-term monitoring of patients with type 2 diabetes are essential to improve survival outcomes after joint replacement surgery.
The findings highlight the importance of comprehensive patient management strategies that account for both metabolic disease and broader health status rather than focusing solely on surgical factors. As hip and knee replacement rates continue to rise worldwide, identifying and managing systemic risks in patients with diabetes will be key to maximizing the benefits of these common orthopedic procedures.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


