- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Antioxidant-Rich Diets Linked to Improved Quality of Life for Young Women Battling Acne Vulgaris, Study Finds
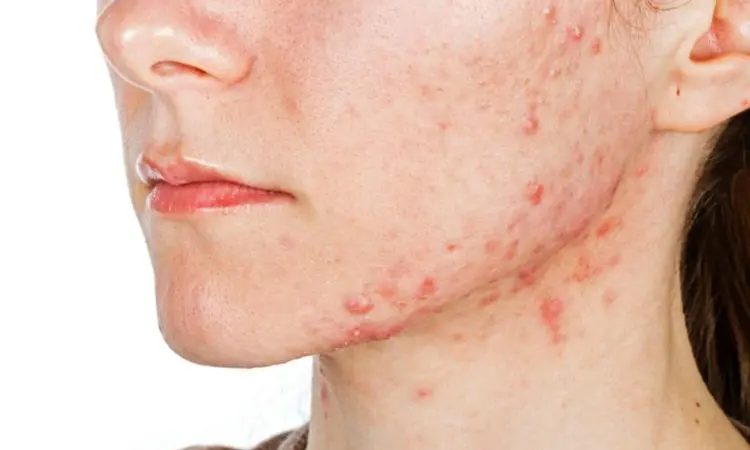
Poland: Acne vulgaris, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, often affects physical appearance and mental well-being. In a promising development, a recent study published in Nutrients Journal suggests that the antioxidant properties of certain diets could offer relief and enhance the quality of life for young women grappling with acne vulgaris.
The study showed that the quality of life (QoL) of young women with acne vulgaris (AV) was impaired. However, there was a reduction in the risk of AV impact on the QoL by approximately 30–32% and the risk of depression by 33% with greater adherence to an antioxidant diet. The dietary antioxidant quality index (DAQI) may be used as a new indicator of diet quality in acne vulgaris.
The DAQI included the following elements: antioxidant vitamins, carotenoids, minerals, phytosterols, polyphenols, lignans, and the total antioxidant capacity of the diet.
Acne vulgaris significantly reduces the QoL of young people, so it becomes critical to look for factors that can improve their QoL. Kinga Zujko-Kowalska, Medical University of Białystok, Białystok, Poland, and colleagues aimed to assess the relationship between dietary antioxidants measured using the new DAQI index and QoL measured using standardized tests.
The study comprised 165 young women with acne vulgaris, mainly students. A self-report survey was used for basic data collection on their anthropometric information, sociodemographic status, and lifestyle.
"Acne vulgaris pathogenesis is not fully known. However, the determination of oxidative stress biomarkers, especially lipid peroxidation in acne patients, confirms the important role of oxidative stress," the researchers wrote.
They added, "Inflammation caused by oxidative stress of the pilosebaceous unit and oxidation of sebum initiates the development of acne. A well-composed diet is a source of various antioxidants (vitamins, minerals, polyphenols) that may support the treatment of acne and improve quality of life."
The energy value of the diet and the content of minerals, vitamins, and carotenoids with the diet's antioxidant activity were estimated using 3-day food diaries and the Diet 6.0 program. The diet's antioxidant potential and the content of phytosterols, polyphenols, lignans, and selenium were calculated based on individual food product consumption and available databases.
While conventional acne treatments focus primarily on topical and systemic medications, integrating dietary modifications can offer patients additional avenues for symptom management. The study underscores the importance of considering lifestyle factors in holistic acne management approaches.
This study has some limitations. First, food intake was assessed based on 3-day food diaries, which did not consider usual eating habits. Second, the available databases on dietary antioxidant potential, polyphenols, selenium, lignans, and phytosterols did not include all foods and dishes, so similar products were used to calculate any missing data.
Reference:
Jankowska, B., & Zujko, M. E. (2023). The Antioxidant Power of a Diet May Improve the Quality of Life of Young Women with Acne Vulgaris. Nutrients, 16(9), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091270
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


