- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
To lose weight- More calories in breakfast, not late-night snacks
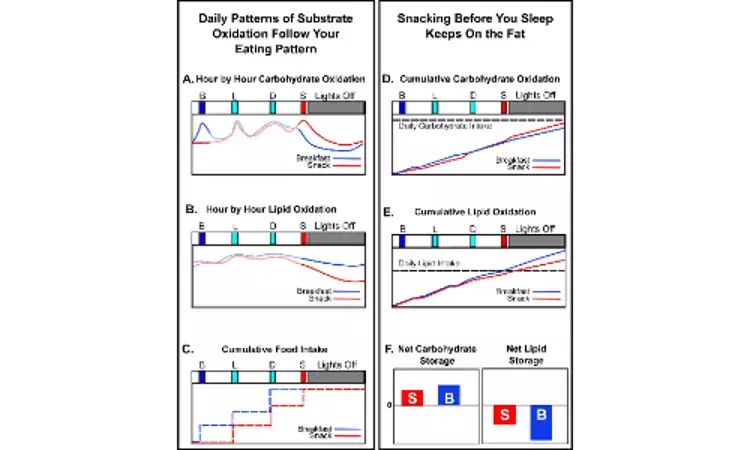 CAPTION (D and E) Cumulative oxidation rates over the 24-h cycle derived from the curves in panels A and B and the experimental data of Fig 3. Panel D shows cumulative CO, while panel E shows cumulative LO. The horizontal dashed lines indicate the daily total intake of carbohydrates (D) and lipids (E) for comparison with the cumulative respective oxidations. (F) Approximate net relative daily storage of carbohydrates and lipids inferred from the data of Fig 3 and the analyses depicted in the other panels of
CAPTION (D and E) Cumulative oxidation rates over the 24-h cycle derived from the curves in panels A and B and the experimental data of Fig 3. Panel D shows cumulative CO, while panel E shows cumulative LO. The horizontal dashed lines indicate the daily total intake of carbohydrates (D) and lipids (E) for comparison with the cumulative respective oxidations. (F) Approximate net relative daily storage of carbohydrates and lipids inferred from the data of Fig 3 and the analyses depicted in the other panels ofA new study published in PLOS Biology has found that daily fast between the evening meal and breakfast will optimize weight management.
Circadian (daily) regulation of metabolic pathways implies that food may be metabolized differentially over the daily cycle. Our daily biological clock and sleep regulate how the food you eat is metabolized; thus the choice of burning fats or carbohydrates changes depending on the time of day or night. Your body's circadian rhythm has programmed your body to burn fat when you sleep, so when you skip breakfast and then a snack at night you delay burning the fat.
Researchers at Vanderbilt University, USA have found that it's not just how many calories you eat, but WHEN you eat them that will determine how well you burn those calories. The study has appeared in PLOS Biology.
The balance between weight gain and weight gain loss is predominantly determined by what you eat, how much you eat, and by how much exercise you get. But another important factor is often neglected… The research conducted by Kevin Kelly, Owen McGuinness, Carl Johnson and colleagues of Vanderbilt University, USA shows that Eating breakfast and avoiding late-evening snacking sustains lipid oxidation.
The researchers monitored the metabolism of mid-aged and older subjects in a whole-room respiratory chamber over two separate 56-hour sessions, using a "random crossover" experimental design. In each session, lunch and dinner were presented at the same times (12:30 and 17:45, respectively), but the timing of the third meal differed between the two halves of the study. Thus in one of the 56-hour bouts, the additional daily meal was presented as breakfast (8:00) whereas, in the other session, a nutritionally equivalent meal was presented to the same subjects as a late-evening snack (22:00). The duration of the overnight fast was the same for both sessions.
Whereas the two sessions did not differ in the amount or type of food eaten or in the subjects' activity levels, the daily timing of nutrient availability, coupled with clock/sleep control of metabolism, flipped a switch in the subjects' fat/carbohydrate preference such that the late-evening snack session resulted in less fat burned when compared to the breakfast session. The timing of meals during the day/night cycle, therefore, affects the extent to which ingested food is used versus stored.
This study has important implications for eating habits, suggesting that a daily fast between the evening meal and breakfast will optimize weight management.
For further reference log on to :
Kelly KP, McGuinness OP, Buchowski M, Hughey JJ, Chen H, Powers J, et al. (2020) Eating breakfast and avoiding late-evening snacking sustains lipid oxidation. PLoS Biol 18(2): e3000622.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000622
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


