- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Vitamin D concentration above 30 ng/mL may protect against gestational diabetes in twin pregnancy: Study
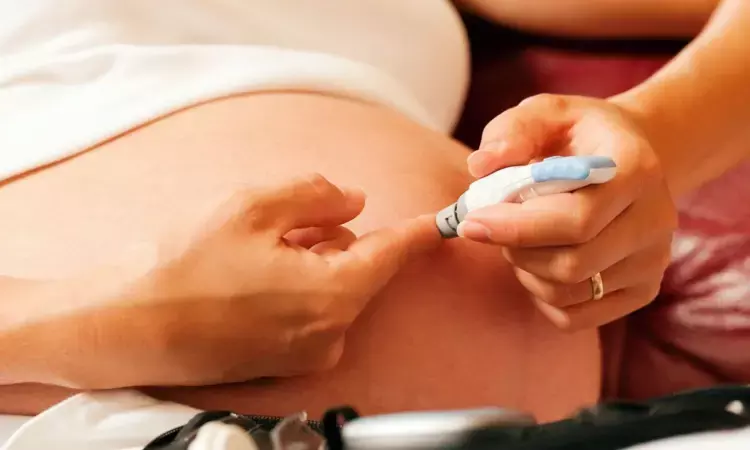
China: A recent study revealed a significantly lowered risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in twin pregnant women with vitamin D concentrations ≥ 30 ng/mL in the second trimester. The findings were published online in Nutrition Journal on April 10, 2024.
Gestational diabetes is a common complication of pregnancy, with significant short-term and long-term effects for both mothers and their offspring. Previous studies have shown the potential benefits of vitamin D in reducing GDM risk, yet not much is known about this association in twin pregnancies. To fill this knowledge gap, Li Wen, Chongqing Health Center for Women and Children, Chongqing, China, and colleagues aimed to investigate maternal vitamin D status in the second trimester and determine its association with the risk of GDM in twin pregnancies.
For this purpose, they conducted a prospective cohort study based on Chongqing Longitudinal Twin Study (LoTiS) data. To measure 25(OH)D concentrations, peripheral blood serum was collected from the mothers in the second trimester. Gestational diabetes was diagnosed at 23–26 weeks of gestation using a 75-g 2-h oral glucose tolerance test. The correlations between vitamin D status and GD risk were also examined.
The study revealed the following findings:
· Of the total participants, 29.9% of women were diagnosed with GDM.
· The mean serum 25(OH)D concentration in the second trimester was 31.1 ± 11.2 ng/mL, and the rate of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency were 23.5% and 18.7%, respectively.
· Compared to women with a 25(OH)D concentration < 30 ng/mL, those with a 25(OH)D concentration ≥ 30 ng/mL had a significantly lower risk of GDM (RR 0.61), especially those who were overweight before pregnancy (RR 0.32).
· The restricted cubic splines model showed an inverted J-shaped relationship between vitamin D concentrations and GDM risk.
In conclusion, the risk of GDM was significantly reduced in those with vitamin D levels ≥ 30 ng/mL in the second trimester in twin pregnant women with vitamin D concentrations < 30 ng/mL in the second trimester. The researchers found a nonlinear association between vitamin D concentrations and GDM incidence, with 30 ng/mL considered as the cutoff for the vitamin D concentration that could significantly reduce GDM risk in twin pregnancies.
"There is a need for further multicenter research to provide more evidence elucidating the relationship between vitamin D and GDM in twin pregnancies," the researchers concluded.
One limitation was the study's single-center design, which limits the findings generalizability of the findings. Another limitation was the lack of accurate data on vitamin D supplementation during the second trimester.
Reference:
Li, Dy., Wang, L., Li, L. et al. Maternal vitamin D status and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in twin pregnancies: a longitudinal twin pregnancies birth cohort study. Nutr J 23, 41 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-024-00944-2
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


