- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Can Detect Meniere Disease, discovers study
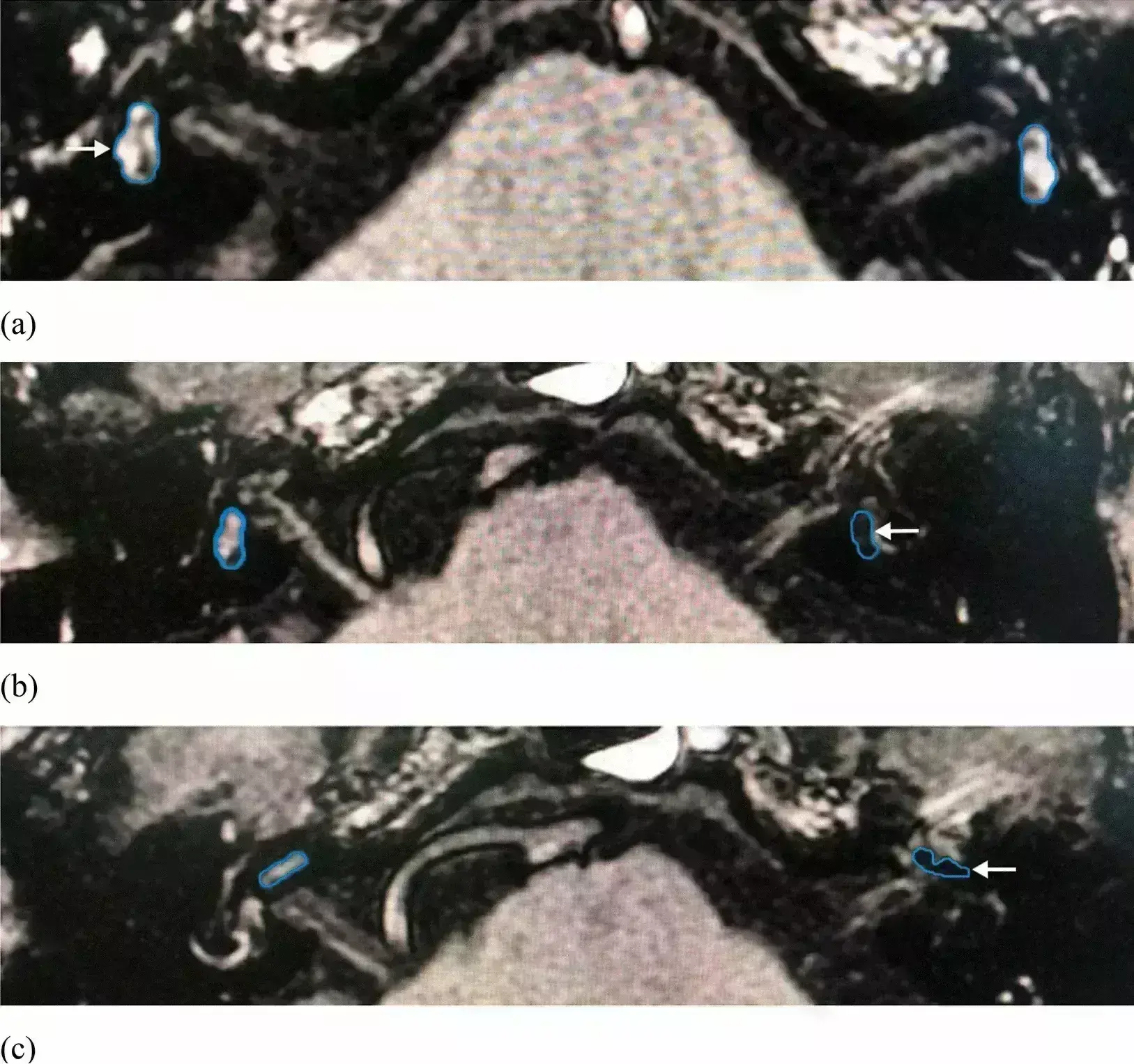
Courtesy by Maoli Duan et al., Scientific Reports
Meniere disease (MD) is an idiopathic inner ear disorder, and endolymphatic hydrops (EH) being considered to be its pathological basis. Currently, there is no gold standard for diagnosing MD. However, a recent study suggests that MRI by intratympanic gadolinium-based contrast media (GBCM) administration (IT-Gd) offers reliable radiological diagnostic criteria for MD. The study findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports on March 30, 2021.
A previous study has reported visualized EH using MRI by intratympanic gadolinium-based contrast media (GBCM) administration (IT-Gd) in patients with MD, and this technique was gradually established for MD diagnosis. However, few studies reported their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity in clinical application. Therefore, Dr Maoli Duan and his team conducted a study to investigate the clinical characteristics and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results of patients with MD and analyzing the relationship between clinical results and MRI findings in MD patients.
In this prospective study, researchers included a total of 117patients with definite MD. The diagnostic criteria were based on the latest guidelines revised in 2015. All the patients received IT-Gd 24 hours prior to MRI by injection through the tympanic membrane. All patients were followed at 1 week, 1, 3 and 6 months after the examination. The primary outcome assessed was diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of MRI findings.
Key findings of the study were:
- Upon analysis, the researchers noted that the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of MRI were 79.2% and 80.7% respectively.
- However, they found no significant correlation between hearing levels and cochlear grading scores, nor vestibular grading scores.
- They also found no significant association between duration of disease and cochlear or vestibular grading scores.
- They noted 26 patients had false-negative MRI results and 21had false-positive MRI results.
- Further, they reported no significant adverse reactions to IT-Gd injection, and all patients healed within one week.
The authors concluded, "Considering the high sensitivity and specificity, IT-Gd MRI offers reliable imaging diagnostic criteria for MD."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


