- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Stellate Ganglion Block Fails to Improve COVID-Related Smell Distortion: JAMA
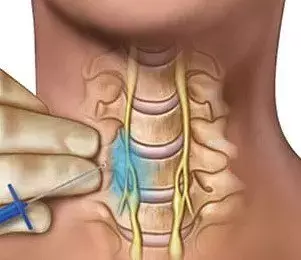
A new study published in the Journal of American Medical Association showed that stellate ganglion block did not reduce COVID-19-induced odor distortion.
A persistent symptom of the post-COVID-19 syndrome that has an incalculable negative impact on quality of life is smell distortion, or parosmia. There is currently no accepted standard for treating this annoying illness. Thus, to ascertain if stellate ganglion block (SGB) is safe and successful in resolving olfactory impairment in individuals with chronic COVID-19-induced parosmia, Nyssa Fox Farrell and colleagues undertook this investigation.
The trial took place at Barnes Jewish Hospital and Washington University in St. Louis between October 2023 and September 2024. A total of 192 volunteers were screened, where 57 were included after fulfilling the eligibility requirements, which included being between the ages of 18 and 70, having self-reported parosmia that occurred at least 6 months following COVID-19 infection, and having a screening score of at least 40 on the Parosmia Olfactory Dysfunction Outcomes Rating [DisODOR] scale. The most frequent explanations for the exclusion of 135 were previous SGB (n = 42) and parosmia resolution or non-COVID-19-induced parosmia (n = 28).
A board-certified anesthesiologist and pain medicine expert administered 6 to 8 mL of active mepivacaine, 1%, or saline, 0.9%, by ultrasound-guided injection at the right or left (randomized 1:1) stellate ganglion. 25% difference between subjects in the percentage of respondents who dropped their DisODOR score by 15 points from the baseline was considered as the primary outcome.
32 people were randomly assigned to SGB (median [range] age, 45 [19-64] years; 25 [81%] female) and 16 were assigned to placebo (median [SD] age, 45 [26-64] years; 13 [81%] female) out of the 48 persons examined in the research. Both groups had comparable times after COVID-19 infection (SGB, 35.3 vs. placebo, 30.6 months; MD = -3.1 months; 95% CI, -10.9 to 3.7).
For SGB, the 3-month response rate was 43% (n = 13), while for the placebo, it was 38% (n = 6; difference, −5%; 95% CI, −32% to 33%). There was no difference in the clinical overall perception of improvement across the groups. Overall, in accordance with the results of this research, SGB is not a better therapy for COVID-19-induced parosmia than a placebo, and as such, it should not be suggested.
Source:
Farrell, N. F., Crock, L. W., Islam, A., Adkins, D., Peterson, A. M., Kallogjeri, D., & Piccirillo, J. F. (2025). Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of COVID-19-induced parosmia: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2025.1304
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


