- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Circadian syndrome associated with prevalence of gallstones in non smokers: BMC Study
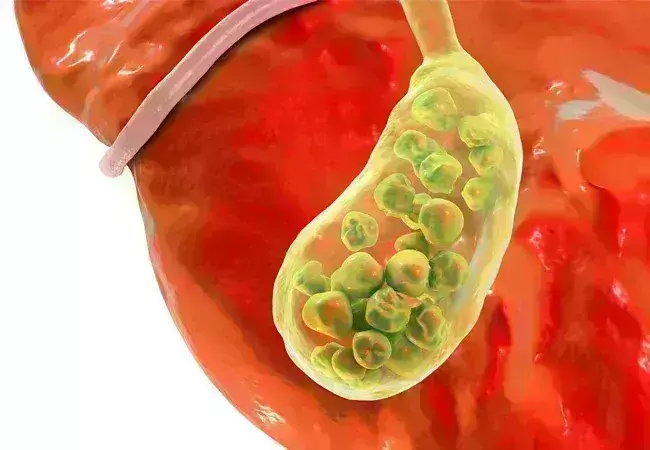
A new study published in the journal of BMC Gastroenterology showed that the occurrence of gallstones was strongly correlated with circadian syndrome, especially in those who did not smoke. About 10% to 20% of individuals worldwide suffer from gallstone disease (GSD) that is one of the most frequent digestive problems in the general population. Symptoms of GSD include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and discomfort in the stomach and abdomen.
Higher incidence and mortality rates from common chronic illnesses such diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and gastrointestinal malignancies have been associated with gallstones. The internal circadian clock generates circadian rhythms which control important bodily physiological processes including metabolism, are produced by transcription factors and gene expression. Chronic conditions including kidney stones, overactive bladder, and stroke are associated with the circadian syndrome. However, nothing is known about the connection between gallstones and circadian disorders. This population-based study by Fenping Liang and colleagues was set to determine if circadian syndrome is linked to gallstones.
This cross-sectional study including a total of 2913 people used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database covering the years 2017 to 2020. The relationship between the prevalence of gallstones and circadian syndrome was investigated using univariate and two adjusted multivariate regression models. The nonlinear connection was described by fitting smoothed curves with the generalized additive model (GAM). To look at possible differences in the association between the risk of gallstones and circadian syndrome, subgroup analyses were also conducted.
The results showed that gallstones and circadian syndrome were positively correlated, with model 2 demonstrating a 117% increase in risk. The frequency of gallstones increased by 76% in model 3. Gallstone risk, however, did not significantly correlate with the number of circadian syndrome components.
Further evidence of linear associations between CircS and gallstone risk was provided by smooth curve fitting based on the GAM. Also, subgroup analysis showed statistically significant correlations between the frequency of gallstones among non-smokers and circadian syndrome. Overall, the results show that among US adults, particularly the people who do not smoke, CircS is positively correlated with an increased incidence of gallstones.
Source:
Liang, F., Qin, T., Hao, Z., Zheng, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2024). Association between circadian syndrome and gallstones in US adult: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017–2020. In BMC Gastroenterology (Vol. 24, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-024-03504-4
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


