- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Diet and lifestyle changes can reduce GERD symptoms beyond acid suppression: JAMA
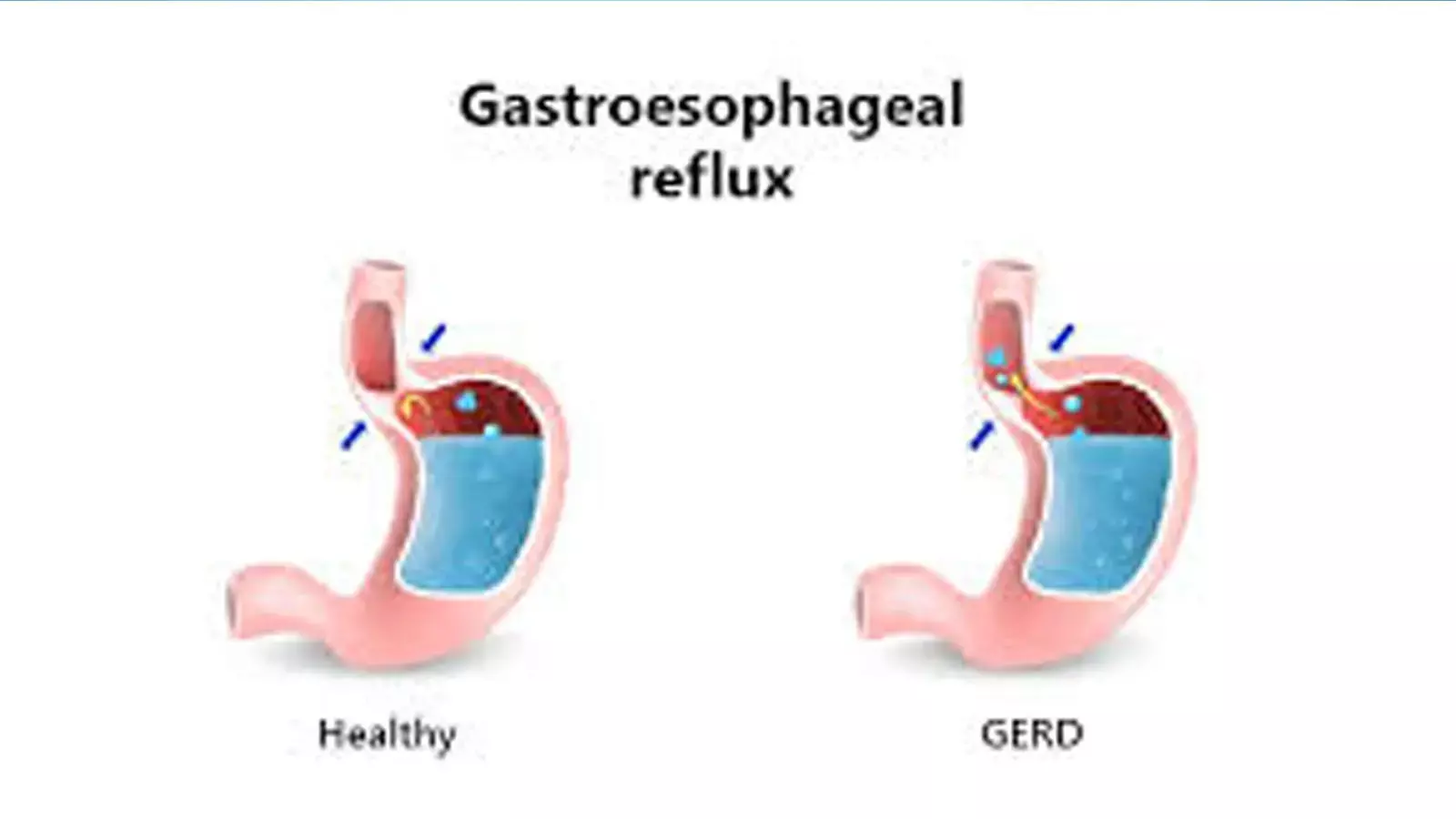
BOSTON - Gastroesophageal reflux disorder is a common condition, affecting about a third of the U.S. population; the main symptom is heartburn and it is often managed with medications.
Data from Nurses' Health Study II suggests that adherence to an anti-reflux lifestyle may prevent many symptoms of gastrointestinal reflux disorder (GERD) in women . Further the decreased risk was evident even in regular users of acid suppressants such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs).
The findings from one of the longest running studies of women's health, show that five diet and lifestyle factors, including regular exercise, can make a significant impact on gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) or heartburn symptoms.
This new study suggests, however, that following diet and lifestyle guidelines may reduce symptoms substantially and could make medication unnecessary for some patients. The study has been published as a letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The five factors include normal weight, never smoking, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity for at least 30 minutes daily, restricting coffee, tea and sodas to two cups daily, and a "prudent" diet.
"This study provides evidence that common and debilitating gastrointestinal symptoms could be well controlled in many cases with diet and lifestyle modifications alone," says Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, the study's senior author. "Given that there are long-term health effects of GERD and lingering concerns about the side effects of medications used to treat it, lifestyle should be considered the best option for controlling symptoms." Chan is a gastroenterologist, chief of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at MGH, and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. The lead author of the research letter is Raaj S. Mehta, MD, gastroenterology fellow at MGH and Harvard Medical School.
The Nurses' Health Study II is a nationwide study established in 1989 whose participants return a detailed health questionnaire twice a year. It began with 116,671 participants and has had follow-up that exceeds 90%. This study included data from almost 43,000 women aged 42 to 62 who were questioned about GERD or heartburn symptoms from 2005 to 2017 -- which represents approximately 390,000 person-years.
The researchers created a statistical model that allowed them to calculate the "population-attributable risk" for GERD symptoms associated with each of the five anti-reflux lifestyle factors -- in other words, they estimated how likely it was that each lifestyle factor lowered risk of experiencing symptoms. They found that following all these guidelines could reduce GERD symptoms overall by 37%. The more of the specific guidelines a woman followed, the lower her risk of symptoms. Among women using common heartburn treatments (proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists), adhering to the guidelines also reduced symptoms.
"We were particularly interested in the effectiveness of physical activity," says Chan. "This is one of the first studies that has demonstrated its effectiveness in controlling GERD." This effect, he suggests, could be due in part to exercise's effect on the motility of the digestive tract. "Being physically active may help with the clearance of stomach acid which causes heartburn symptoms," he says.
For further reference log on to:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


