- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dupilumab improves histologic outcomes of eosinophilic esophagitis: NEJM
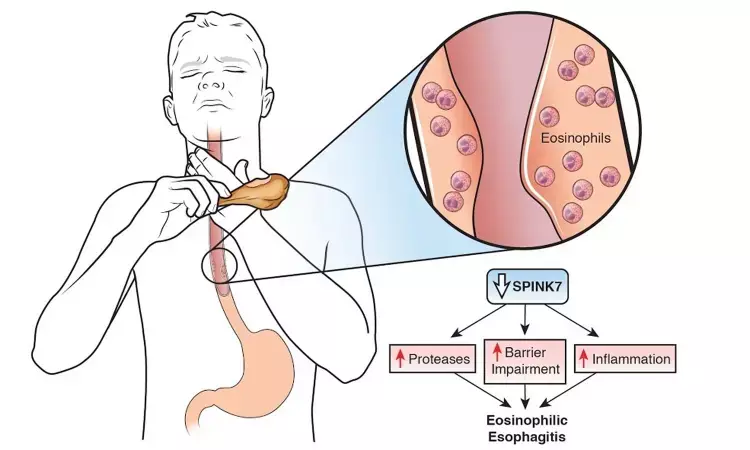
A new study published in The New England Journal of Medicine suggests that subcutaneous dupilumab given weekly to individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis improved histologic results and relieved symptoms of illness.
Dupilumab is a completely human monoclonal antibody that inhibits interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 signaling, both of which play important roles in eosinophilic esophagitis. As a result, Evan Dellon and colleagues undertook this trial to investigate the effectiveness of dupilumab in persons with eosinophilic esophagitis.
Patients 12 years of age and older participated in a three-part phase 3 trial, in which they were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive subcutaneous dupilumab at a weekly dose of 300 mg or placebo (Part A) or in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive 300 mg of dupilumab either weekly or every two weeks or weekly placebo (Part B) up to week 24. The Part A-C group, which consisted of the eligible patients from Part B, got dupilumab at a weekly dose of 300 mg until week 52. Part C, which also included the eligible patients from Part A, is still ongoing. Histologic remission (6 eosinophils per high-power field) and the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ) score change from baseline were the two main end objectives at week 24. (range, 0 to 84, with raised values denoting more frequent or more severe dysphagia).
The key findings of this study were:
1.Histologic remission occurred in Part A in 2 of 39 patients (5%) who got placebo and in 25 of 42 patients (60%) who received weekly dupilumab.
2.In Part B, histologic remission was seen in 49 of 81 patients (60%) who received dupilumab every two weeks, 47 of 80 patients (59%) who received weekly dupilumab, and 5 of 79 patients (6%) who received placebo (deviation between weekly dupilumab and placebo, 54 percentage points; 95% CI, 41 to 66 [P0.001]; difference among both dupilumab and placebo, 56 percentage points; 95%)
3.At baseline, the mean (SD) DSQ scores were 33.6±12.41 in Part A and 36.7±11.22 in Part B.
4.The scores improved with weekly dupilumab compared to placebo, with differences of -12.32 in Part A and -9.92 in Part B, but not with dupilumab every two weeks.
5.Serious side effects happened in 9 patients during the Part A or B treatment periods (7 patients who received weekly dupilumab, 1 patient who received dupilumab every 2 weeks, and 1 patient who received placebo), as well as in 1 patient in the Part A-C group during the Part C treatment period who received weekly dupilumab in Part A and placebo in Part C.
Reference:
Dellon, E. S., Rothenberg, M. E., Collins, M. H., Hirano, I., Chehade, M., Bredenoord, A. J., Lucendo, A. J., Spergel, J. M., Aceves, S., Sun, X., Kosloski, M. P., Mannent, L. P., Laws, E., Akinlade, B., … Shabbir, A. (2022). Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. In New England Journal of Medicine (Vol. 387, Issue 25, pp. 2317–2330). Massachusetts Medical Society. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2205982
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


