- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Human intestinal spirochetosis may be a sexually transmitted disease
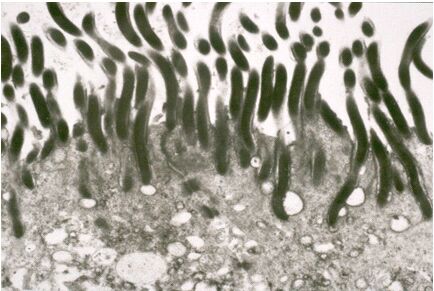
Human intestinal spirochetosis (HIS) is a possible cause of chronic diarrhoea and affects mainly men who have sex with men (MSM) and people living with HIV, suggest a study published in the SAGE journals on November 24, 2020.
Colonization of the colorectal mucosa with spirochetes is very rare. Owing to the small number of cases, it is not clear from the currently available publications whether spirochetes colonizing the colorectal mucosa are harmless commensals or pathogenic organisms. Diagnosis is based on colon biopsy, where spirochetes can be observed on the luminal surface, especially with the Warthin-Starry stain or similar silver stains.
Researchers of Spain conducted a retrospective, descriptive study in patients with HIS diagnosed 2009-2018 at two sexually transmitted infections centres in Barcelona. A total of 6 MSM with HIS, were included in the study among which 3 of them were also living with HIV. Median age at diagnosis was 31.5 (interquartile range, 29.5-49.25) years. Researchers reported History of condomless anal intercourse in five patients and previous oro-anal sex practice in 4 patients. They also reported one had concomitant Chlamydia trachomatis (nonlymphogranuloma venereum), 2 had rectal gonorrhea and none of them had syphilis. The medical histories were reviewed to gather epidemiological, clinical, and diagnostic variables. Predominant symptoms reported were diarrhoea (5), anal discharge (2), abdominal pain (2), anal bleeding (2), flatulence (2)
They found all cases were diagnosed by a Warthin-Starry stain on a colon biopsy specimen, and they also found mild inflammatory changes in all 5 cases. Five patients were treated with metronidazole and one received intramuscular benzathine penicillin G, 2.4 million units and all the patients were recovered from the HIS.
After analyzing the result the authors concluded, "Human intestinal Spirochetosis (HIS) should be considered in patients with chronic diarrhoea who report risky sexual practices and/or concomitant Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)".
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


