- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease independently linked to elevated gout risk: Study
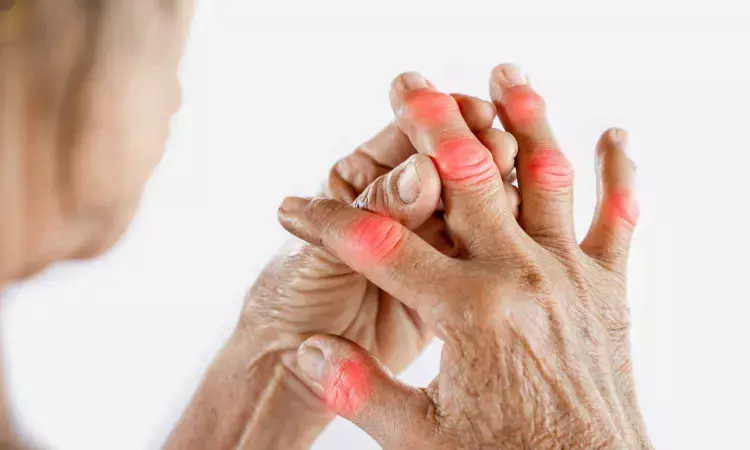
A new study published in the European Journal of Medical Research showed that gout risk was 71% greater in individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MASLD) than in those without.
A growing public health problem, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is intimately related to obesity, insulin resistance, and other elements of metabolic syndrome. Growing research indicates that MAFLD may considerably raise the risk of extrahepatic disorders, such as gout, in addition to liver-related problems. MAFLD and gout, a type of inflammatory arthritis brought on by high blood uric acid levels, overlap metabolic pathways, especially in regard to insulin resistance and lipid abnormalities.
Investigating this relationship might potentially reveal common processes and possible treatment targets. The relationship between MASLD and incident gout risk is thoroughly investigated in this first prospective cohort research in Europe.
This study used UK Biobank data (n = 402,083 after exclusions), omitting individuals with baseline gout, arthritis, hepatitis B/C, alcohol-related liver illness, or incidents during the first two-year follow-up. MASLD–gout relationships were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models, and cumulative incidence was represented by Kaplan–Meier curves.
When compared to their non-MASLD peers, MASLD patients had a 71% higher incidence of gout (HR = 1.71, 95% CI 1.59–1.83, P < 0.0001). Subgroup analyses showed significant correlations across demographics, with older persons having a lower risk (≥65 years: HR = 1.55 vs. <65 years: HR = 1.86).
Ironically, those without central obesity, diabetes, or hypertension showed a greater chance of developing gout than people with these conditions. Over time, the cumulative incidence of gout was considerably higher among MASLD patients (P<0.001). Overall, MASLD was significantly linked to a higher incidence of gout. MASLD was still linked to a markedly higher incidence of gout even after controlling for covariates.
Gout in MASLD patients may be influenced by a number of factors, including sex, age, BMI, alcohol and smoking status, hypertension, diabetes, and central obesity. These results imply that elucidating this link may have significant therapeutic consequences for gout prevention and treatment, as well as preventing the elevated risk of gout-induced chronic illnesses by MASLD-focused therapies.
Source:
Liu, X., Wang, Y., Song, H., Tian, Z.-B., Wang, Y.-G., Yu, Q., Li, C., Niu, Q., Zhu, X.-J., & Chen, Y. (2025). Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and the risk of gout: a UK Biobank prospective cohort study. European Journal of Medical Research, 30(1), 1027. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-025-03298-5
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


