- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Metabolic dysfunction linked to surge in gallstone disease, finds study
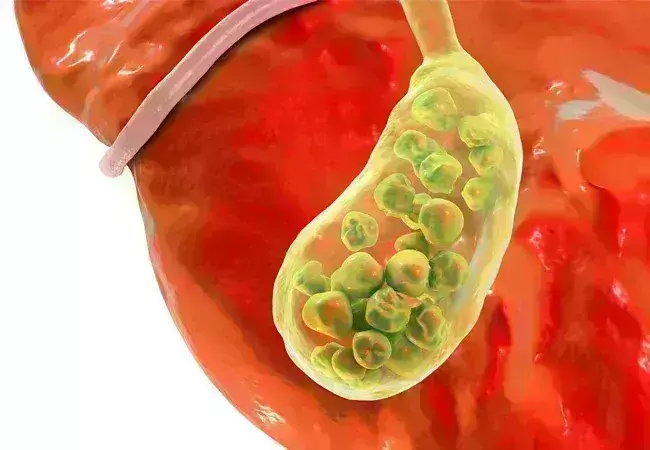
A new study published in the Journal of Digestive Diseases found a significant increase in gallstone disease in the U.S., likely driven by the growing prevalence of metabolic disorders. Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, this study found strong associations between gallstones and conditions like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
Gallstone disease can cause problems such as acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, and pancreatitis, even though some people with the condition have no symptoms. In order to reduce morbidity and mortality, rare but serious complications such gallstone ileus, gallbladder perforation, and Mirizzi syndrome must be treated promptly.
Ethnicity, advanced age, female gender, and lifestyle choices such a high-fat diet and sedentary activity are risk factors for gallstones. The incidence of gallstones is significantly increased by certain metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus (DM), obesity, and insulin resistance (IR). Thus, this study examined the relationship between gallstone disease and prevalent metabolic diseases in a nationally representative sample of Americans.
This research examined information gathered between 2017 and 2020 from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). 6,164 individuals, or 17,14,07,370 persons, who met the eligibility requirements were included. Multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to examine the relationships between gallstone disease and 6 metabolic illnesses while taking any confounding variables into consideration.
The prevalence of gallstone disease was 10.9% overall, with a female preponderance (75.1% vs. 24.9%, p < 0.001) and an increase with age (mean age with vs. without gallstones: 56.435 years vs. 46.896 years, p < 0.001).
A higher risk of gallstone formation was significantly linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obesity, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus; the corresponding adjusted odds ratios (OR) were 1.523 (95% CI 1.180–1.965, p = 0.002), 1.733 (95% CI 1.265–2.374, p = 0.001), 1.466 (95% CI 1.203–1.785, p = 0.001), and 1.522 (95% CI 1.165–1.989, p = 0.003).
These correlations were stronger among females and those under 60 years old. There were no noteworthy correlations seen with either hyperlipidemia or hyperuricemia. Overall, gallstone disease is linked to obesity, diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and hypertension in American adults; this association is much stronger in women and those under 60. To assess the causal link and the underlying processes behind these disorders, more research is required.
Source:
Tang, Y. F., Su, Y. T., Liang, L. J., Feng, Y., Huang, X. J., Xiang, X. L., & Liang, Z. H. (2025). Association between metabolic dysfunction and gallstone disease in U.s. adults: An analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Journal of Digestive Diseases, 26(3–4), 158–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-2980.13349
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


