- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Plasmapheresis may not Reduce Organ Failure among patients with hypertriglyceridemia associated pancreatitis
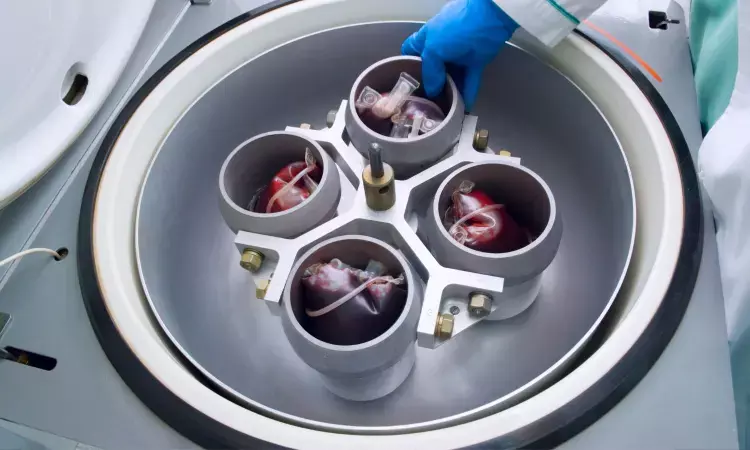
An Original Investigation on Gastroenterology and Hepatology published on June 28, 2023, in JAMA Network Open entitled "Early Plasmapheresis Among Patients With Hypertriglyceridemia–Associated Acute Pancreatitis" by lead author Cao et al. have mentioned that plasmapheresis does not confer any clinical benefit in managing hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis or HTG-AP and is associated with potential complications.
In this study, researchers found no association between plasmapheresis and the incidence and duration of organ failure. Plasmapheresis may not decrease triglyceride levels more efficiently than conventional medical therapy. These findings of the present study are comparable with those conducted by Chen et al. and Miyamoto et al.
It is already known that there is an increasing incidence of hypertriglyceridemia–associated acute pancreatitis (HTG-AP). Plasmapheresis is theoretically effective in removing triglyceride from plasma, but there needs to be more clarity on whether it has clinical benefits.
This multicenter, prospective cohort study enrolled patients from 28 sites across China. HTG-AP patients were admitted within 72 hours from the onset of the disease. The primary outcome was organ failure–free days to 14 days of enrolment, while other measures for organ failure, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, duration of ICU and hospital stays, the incidence of infected pancreatic necrosis, and 60-day mortality were the secondary outcomes.
The key results of this study are:
- Two hundred sixty-seven patients of mean age 37 years enrolled had a history of HTG-AP.
- Of these patients, 211 underwent conventional medical treatment, and 56 underwent plasmapheresis.
- No difference was detected concerning organ failure–free days between patients undergoing plasmapheresis or not.
- Researchers reported more ICU admission in the plasmapheresis group.
Study strength includes a large study size, reduced selection bias and valid comparison.
They said, "We found that early plasmapheresis is not associated with the incidence and duration of organ failure but with a greater need for ICU admission."
Further reading:
Cao L, Chen Y, Liu S, et al. Early Plasmapheresis Among Patients With Hypertriglyceridemia–Associated Acute Pancreatitis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(6):e2320802. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20802
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


