- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Schizophrenia and MDD causally linked to increased constipation risk, discovers study
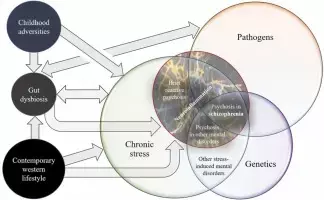
Schizophrenia and MDD causally linked to increased constipation risk, discovers study published in the Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology.
Psychiatric disorders have been associated with Constipation in observational studies, although their causal relationships remain uncertain. We used Mendelian randomization analysis to infer causality between Schizophrenia and Major Depressive Disorder with Constipation.
The exposure of interest was Psychiatric disorders, including Schizophrenia (SCZ) and Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). Summary statistics for psychiatric disorders were recruited from the PGC, SCZ (30,490 cases and 312,009 controls), MDD (170,756 cases and 329,443 controls), whereas Constipation summary genetic data were obtained from a FinnGen involving 17,246 cases and 201,546 controls.
The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method was used as the primary analysis to assess the causal relationship between SCZ and MDD with Constipation. Results: LDSC indicated that Constipation was genetically correlated with Psychiatric disorders (r g range: |0.04-0.05). The Mendelian randomization analysis indicated that there was significant evidence that genetically determined SCZ (OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.02-1.07, P<0.01) and MDD (OR = 1.21, 95% CI = 1.10-1.33, P<0.01) were statistically significantly causally associated with the risk of Constipation.
SCZ effects remained within the range of practical equivalence (ROPE). The Mendelian randomization analysis suggested that SCZ and MDD increase the risk of Constipation. However, the association between SCZ and constipation, predominantly within the ROPE range, suggested only limited clinical implications.
Reference:
Liu J, Huang Y, Fu X, Wei J, Wei P. Associations of Schizophrenia and Major Depressive Disorder with Constipation: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 26;17:349-357. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S485504. PMID: 39618883; PMCID: PMC11608058.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


