- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
How Intravascular Imaging With IVUS Is Transforming Coronary Artery Disease Management- Dr Ajith Pillai
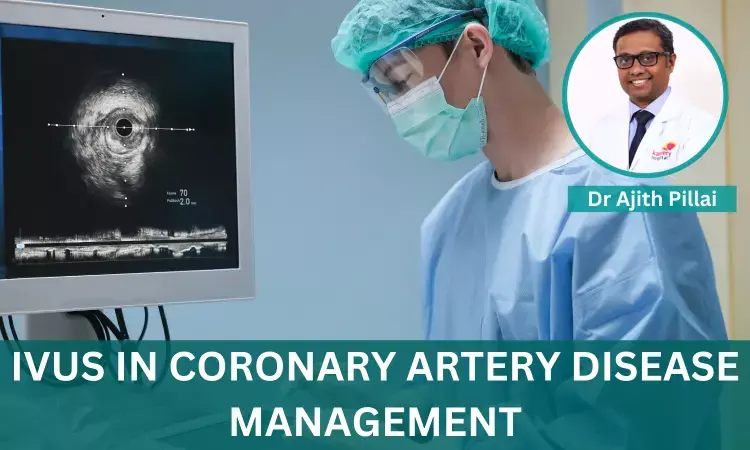
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a minimally invasive imaging technique that allows cardiologists to visualise the inside of coronary arteries in real-time. It is a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing coronary artery disease (CAD), the leading cause of death worldwide.
IVUS uses a miniature ultrasound transducer mounted on the tip of a thin catheter. The catheter is inserted into an artery through a small incision in the wrist or groin and threaded up to the heart. The ultrasound transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the arterial walls and are reflected to the transducer. These reflected sound waves are then converted into images of the inside of the artery.
This approach provides several advantages over traditional coronary angiography, the other main imaging technique used to diagnose CAD. Angiography uses X-rays to create images of the coronary arteries, but it is limited in its ability to assess the severity of plaque buildup and the structure of the arterial wall.
IVUS, on the other hand, can provide detailed images of the plaque, including its composition, thickness, and distribution. It can also be used to measure the size of the coronary artery lumen and the degree of stenosis.
IVUS has several applications in the management of CAD, including:
- Diagnosis: IVUS can be used to diagnose CAD and assess the severity of plaque buildup. This information can be used to determine the best course of treatment, such as medication or interventional procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
- Guiding PCI: IVUS can be used to guide PCI, a procedure to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. IVUS can help cardiologists select the appropriate stent size and position the stent accurately.
- Evaluating stent results: IVUS can be used to evaluate the results of PCI and to identify any complications, such as stent malapposition or thrombosis.
- Monitoring disease progression: IVUS can be used to monitor disease progression over time and to identify patients at high risk for future events.
Benefits of IVUS-guided PCI:
IVUS-guided PCI has a number of benefits over standard PCI, including:
- Reduced risk of stent thrombosis: IVUS-guided PCI has been shown to reduce the risk of stent thrombosis, a serious complication that can occur after PCI.
- Improved stent apposition: IVUS can be used to ensure that the stent is fully expanded and apposed to the arterial wall. This helps to reduce the risk of restenosis, a narrowing of the artery that can occur after PCI.
- Better long-term outcomes: IVUS-guided PCI has been shown to improve long-term outcomes in patients with CAD, including reduced risk of death and myocardial infarction (heart attack).
IVUS in the Future of CAD Management:
IVUS is an evolving technology, and new applications for IVUS are being developed all the time. For example, IVUS is now being used to develop and evaluate new stents and other interventional devices. IVUS is also being used to study the biology of atherosclerosis and to identify new biomarkers for CAD.
As IVUS technology continues to improve, it is likely that IVUS will play an even greater role in the management of CAD in the future. IVUS is a valuable tool for cardiologists to diagnose, guide, and evaluate PCI, and it has been shown to improve long-term outcomes in patients with CAD.
Prof Dr Ajith Pillai MBBS, MD (Doctor of Medicine), DM (Cardiology), FIC (Germany), FRCP(Lon), FRCP(Edin), FRCP(Glasgow), FACC, FSCAI is an Interventional Cardiologist and the Head of Department (Cardiology) at Kauvery Hospital, Chennai having over 26 years of experience in the field of cardiology. He specialises in Complex CHIP PCI and MCS, Advanced invasive cardiac imaging, Congenital Heart Disease and GUCH interventions, Interventional cardiac electrophysiology, Complex TAVR, Basilica, and Mitral and Tricuspid repair.


