- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rare case of Disseminated Fusariosis reported in NEJM
 Courtesy NEJM
Courtesy NEJMDr Jacques Sevestre and Dr Lora Kopec at IHU Méditerranée Infection, Marseille, France have reported a case of Disseminated Fusariosis.The case has been published in the New England journal of Medicine.
Disseminated fusariosis (DF) is considered an extremely rare infection and has reached a stable incidence rate, but its high mortality rate and the lack of an optimal management protocol have raised increasing interest in this mycosis.
Invasive fungal infections are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised patients, such as subjects with hematological malignancies and patients who underwent to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) or solid organ transplantation (SOT). Fusarium spp. cause a broad spectrum of infections in humans.Early diagnosis and treatment is very important to improve the prognosis, because these infections in immunodepressed hosts have a high mortality rate.
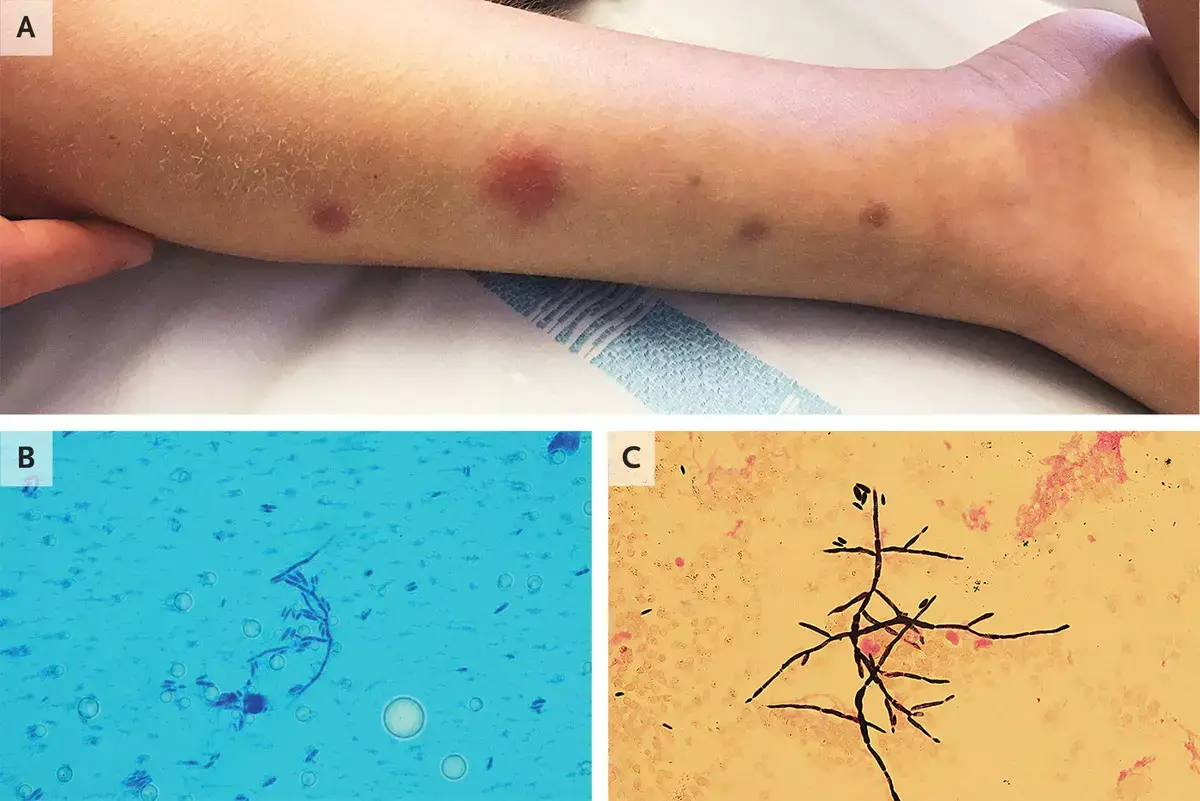
According to history a 8-year-old boy presented with subcutaneous nodules associated with a 1-week history of fever 2 months after starting treatment for relapsing B-cell leukemia. He had had pancytopenia for 57 days, and laboratory studies showed a hemoglobin level of 7.5 g per deciliter (reference range, 11.5 to 14.5), a white-cell count of 200 per cubic millimeter (reference range, 5000 to 11,000), and a platelet count of 12,000 per cubic millimeter (reference range, 150,000 to 400,000). Fevers persisted despite the initiation of broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic and antifungal treatment, and 1 week later, the subcutaneous nodules developed. Physical examination revealed nodules ranging from 5 to 18 mm in diameter on the chest, back, arms, and legs (Panel A). A biopsy specimen of a nodule was obtained. Microscopic examination of a dry smear stained with lactophenol cotton blue revealed septated hyphae and spores (Panel B), and Fusarium dimerum was grown in culture. Gram's staining of a blood culture revealed hyphae and spores (Panel C), and cultures also revealed F. dimerum. The patient completed a prolonged course of treatment with antifungal therapy. His fever resolved within 11 days, and the skin lesions resolved within 20 days.
For further reference log on to:
N Engl J Med 2020; 382:e64
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


