- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sleep extension may improve cardiometabolic functioning, hydration status and sedentary behavior in college students
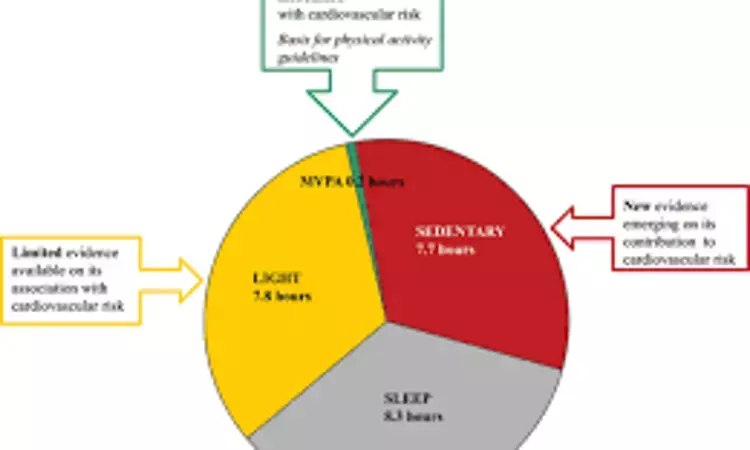
Sleep extension may improve cardiometabolic functioning, hydration status and sedentary behavior in college students suggests a new study published in the Sleep health.
Short sleep duration is associated with poor physical health in college students. Few studies examine the effects of sleep extension on physical health in this population, who are susceptible to sleep loss. We examined health effects of a 1-week, 1-hour nightly sleep extension in college students.
Twelve healthy undergraduate college students (83% female; age 20.2 ± 1.5years) completed a study consisting of sleeping typically for 1week ("Habitual"), then extending sleep by ≥1 hour/night during the second week ("Extension"). Sleep and physical activity actigraphy were collected throughout. Following each week, participants completed cardiometabolic assessments including a meal response and provided a urine sample for markers of hydration.
RESULTS
In Extension compared to Habitual, average sleep duration increased (mean change±SEM, +42.6 ± 15.1 minutes; p = .005), while subjective sleepiness (-1.8 ± 0.8 units; p = .040), systolic blood pressure (-6.6 ± 2.8 mmHg; p = .037), postprandial glucose area under the curve (-26.5 ± 10.2 mg/dL × h; p = .025) and time to baseline (-83.0 ± 46.4 minutes; p = .031) after the meal response, sedentary time (-44.3 ± 15.7 minutes; p = .018), and percentage of wake in moderate-to-vigorous activity (-0.89% ± 0.35%; p = .030) decreased. Participants who increased average sleep duration by ≥20 minutes (n = 9) were better hydrated according to urine osmolality (-187.0 ± 68.4 mOsm/kg; p = .026) and specific gravity (-0.01 ± 0.002 g/mL; p = .012) and had reduced odds of dehydration according to urine osmolality (≥800 mOsm/kg; -67%; OR=0.03; p = .035).
This pilot study's findings suggest that sleep extension may improve cardiometabolic functioning and hydration, and alter sedentary behavior and physical activity, in college students. Sleep extension may be employed to improve multiple aspects of health in this sleep-deprived population.
Reference:
Mathew, Gina Marie, et al. "Effects of a 1-hour Per Night Week-long Sleep Extension in College Students On Cardiometabolic Parameters, Hydration Status, and Physical Activity: a Pilot Study." Sleep Health, 2023.
Keywords:
Sleep, extension, may, improve, cardiometabolic, functioning, hydration sedentary, behavior, college students, Mathew, Gina Marie, Sleep health
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


