- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Gout under reported finding in patients of peritoneal and hemodialysis
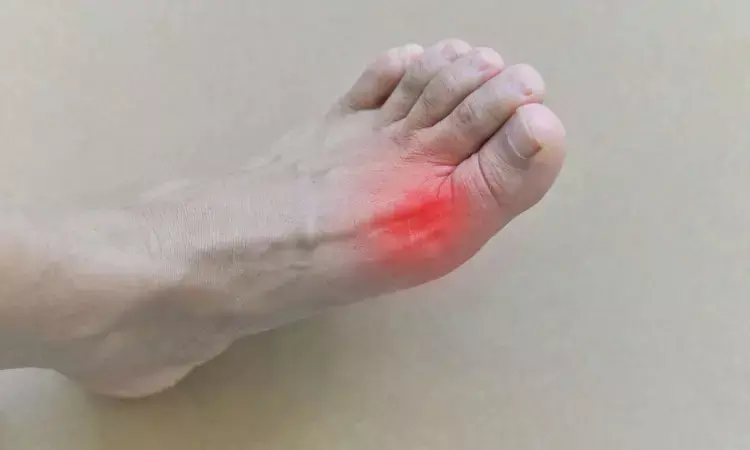
North America: A new study found that gout occurs frequently and is often underreported in patients undergoing hemo and peritoneal dialysis. The study results were published in the journal Kidney360.
An increased frequency of Gout in renal disease patients causes a significant burden on quality of life. There is huge uncertainty regarding the prevalence of gout, and its association with outcomes in hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD) populations in North America. Hence researchers conducted a study to understand the same.
The study was carried out using data from North American cohorts of 70,297 HD patients (DOPPS, 2012-2020) and 5117 PD patients (PDOPPS, 2014-2020). Participants were considered to have gout if they had an active prescription for colchicine or febuxostat; or an active prescription for colchicine, febuxostat, or allopurinol; or had an active prescription for colchicine, febuxostat, or allopurinol, or prior diagnosis of gout. A comparison of outcomes among patients with or without gout was done using propensity score matching. Outcomes included erythropoietin resistance index (ERI=erythropoiesis stimulating agent dose per week/(hemoglobin×weight)), all-cause mortality, hospitalization, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
Results:
- The was a 13% prevalence of gout in HD and 21% in PD which was highest among incident dialysis patients.
- Description of the previous history of gout was rare, and identification of gout defined by colchicine (2%-3%) or febuxostat (1%) prescription was less frequent than by allopurinol (9%-12%).
- Both HD and PD patients with gout (versus no gout) were mostly old males with higher body mass index and a higher prevalence of cardiovascular comorbidities.
- Urate-lowering therapy was prescribed to nearly half of the patients with a gout history.
- After propensity score matching, mean ERI was 3%-6% higher for gout versus non-gout patients while there was minimal evidence of association with clinical outcomes or PROs.
Thus, gout was a frequent presentation in PD and HD patients without any adverse clinical outcomes in North America but was frequently underreported.
Further reading: Guedes M, Zhao J, LaMoreaux B, et al. Gout Prevalence, Practice Patterns, and Associations with Outcomes in North American Dialysis Patients. Kidney360. 2023;4(1):54-62. doi: 10.34067/KID.0005392022
Dr Kartikeya Kohli is an Internal Medicine Consultant at Sitaram Bhartia Hospital in Delhi with super speciality training in Nephrology. He has worked with various eminent hospitals like Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Sir Gangaram Hospital. He holds an MBBS from Kasturba Medical College Manipal, DNB Internal Medicine, Post Graduate Diploma in Clinical Research and Business Development, Fellow DNB Nephrology, MRCP and ECFMG Certification. He has been closely associated with India Medical Association South Delhi Branch and Delhi Medical Association and has been organising continuing medical education programs on their behalf from time to time. Further he has been contributing medical articles for their newsletters as well. He is also associated with electronic media and TV for conduction and presentation of health programs. He has been associated with Medical Dialogues for last 3 years and contributing articles on regular basis.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751




