- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Kaempferol Protects Against High Glucose-Induced Cell Damage, Suggests Study
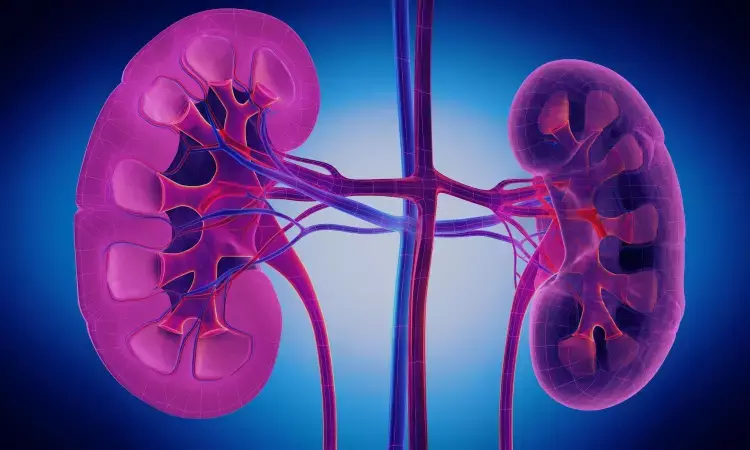
China: Researchers have found in a new study that kaempferol reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by high glucose (HG), with its protective effects linked to Sirt3 expression and activation of the ROS-sensitive Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway. These findings highlight the potential of this dietary flavonoid as a therapeutic candidate for diabetic nephropathy, a major complication of diabetes marked by kidney damage.
- HK-2 cells exposed to high glucose and treated with 10 µM kaempferol showed significantly higher viability than cells exposed to high glucose alone.
- Kaempferol reversed high-glucose–induced reductions in the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) and catalase.
- Treatment lowered levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Markers of apoptosis, including the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and cleaved caspase-3, were decreased.
- Western blot and real-time PCR showed increased Sirt3 expression and higher phosphorylation ratios of Akt and FoxO3a, indicating activation of the ROS-sensitive Akt/FoxO3a pathway.
- Downregulation of Sirt3 weakened kaempferol’s protective effects, leading to reduced cell viability and increased ROS levels.
- Findings indicate Sirt3 is a key mediator of kaempferol’s antioxidant and anti-apoptotic actions.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


