- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MR study doesn't support causal association between serum vitamin D levels and urolithiasis
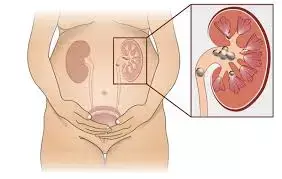
MR study doesn't support a causal association between serum vitamin D levels and urolithiasis.
In light of inconsistent evidence from previous observational studies regarding the correlation between serum vitamin D levels and urolithiasis, this study aimed to investigate the genome-wide causal association between genetically predicted serum 25(OH)D levels and urolithiasis using the Mendelian randomization (MR) approach. In this study, we utilized genome-wide association studies (GWAS) summary statistics from the UK Biobank and SUNLIGHT consortium for serum vitamin D levels, as well as urolithiasis data from FinnGen. We employed bidirectional two-sample MR analysis to evaluate potential causal relationships.
The primary MR analysis relied on the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method, supplemented by MR-Egger, weighted median, and weighted mode approaches. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to ensure result robustness, including Cochran’s Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, leave-one-out tests, and MR pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO) test.
Results: The MR analysis indicated no significant causal effects of serum 25(OH)D levels on urolithiasis [IVW method: (kidney and ureteral stones: OR = 1.134;95% CI, 0.953 to 1.350, p = 0.155; lower urinary tract stones: OR = 1.158; 95% CI, 0.806 to 1.666, p = 0.428)]. However, according to the IVW results, genetically predicted kidney and ureteral stones were associated with decreased serum 25(OH)D levels (beta = -0.025; 95% CI, -0.048 to -0.003; p = 0.028), while they did not indicate a causal effect of lower urinary tract stones on serum 25(OH)D levels (beta = -0.002; 95% CI, -0.013 to -0.008; p = 0.662). A sensitivity analysis suggested the robustness of these causal associations.
The MR study did not provide evidence supporting a causal association between serum 25(OH)D levels and urolithiasis among individuals of European descent. However, there might exist a negative causal association between kidney and ureteral stones and serum 25(OH)D levels.
Reference:
Zhang, QF., Zhang, HZ., Wang, S. et al. Causal association of serum vitamin D levels with urolithiasis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Nutr 64, 39 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-024-03553-1
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


