- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Total bilirubin may Predict Mortality in maintenance hemodialysis Patients: Study
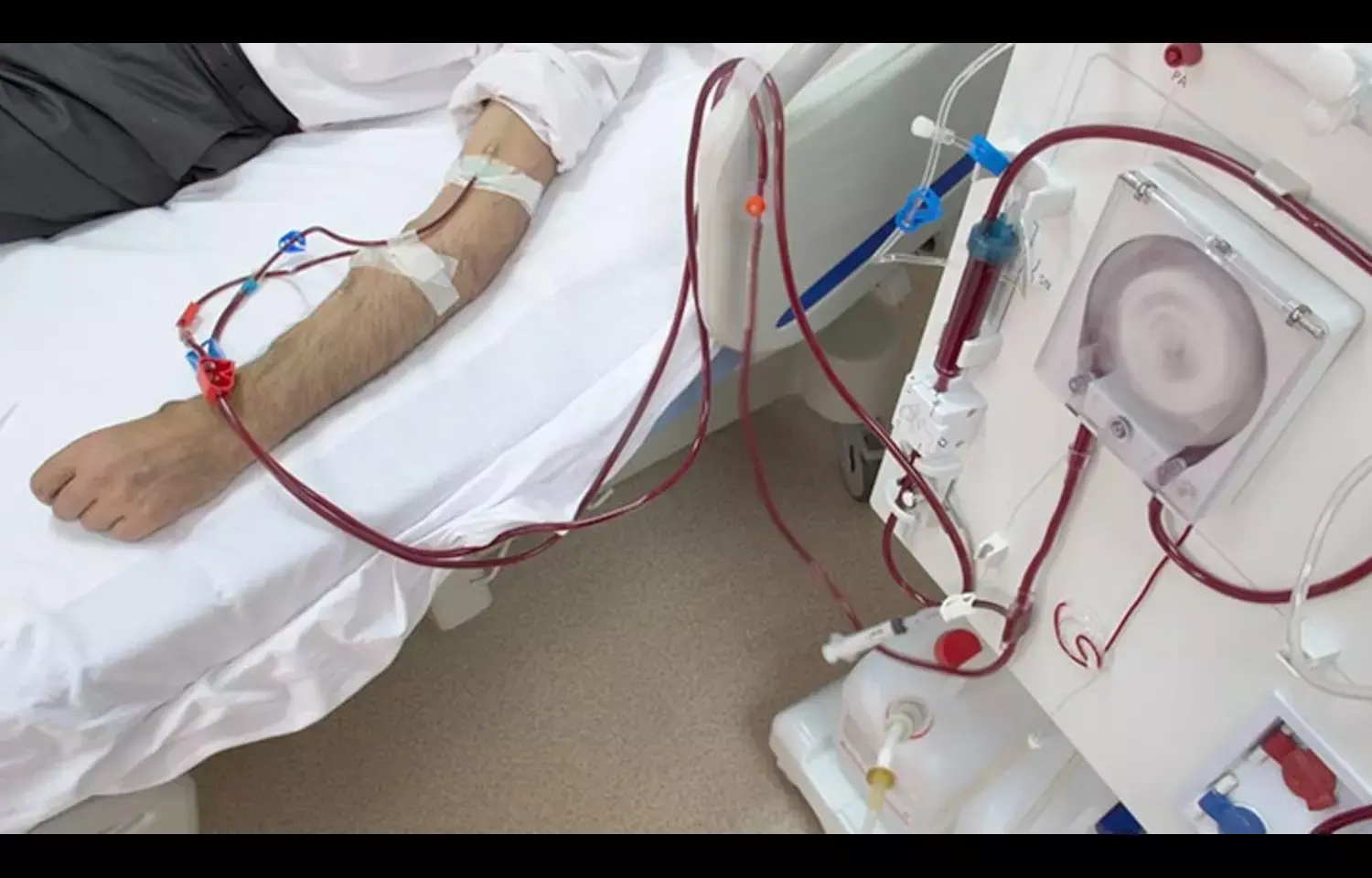
A new study published in BMC Nephrology examined the role of total bilirubin as a potential clinical marker in adults undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Researchers found that total bilirubin functioned as an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in this population. Their analysis showed that patients with lower bilirubin levels faced a higher mortality risk, suggesting that bilirubin may reflect underlying oxidative stress or impaired physiological resilience in chronic kidney disease. The authors highlighted that bilirubin, a routinely measured parameter, may offer additional prognostic value without adding cost or complexity to clinical workflows.
The investigation also explored whether the predictive strength of bilirubin varied by age. Findings indicated that the association between bilirubin levels and mortality appeared stronger in non-elderly hemodialysis patients. This pattern suggests that younger individuals on long-term dialysis may be more physiologically sensitive to bilirubin-related pathways or that bilirubin may better capture risk in patients who have fewer competing comorbidities. While the biological mechanisms remain to be clarified, the researchers proposed that oxidative balance and inflammatory load—both reflected in bilirubin physiology—may play a larger role in survival outcomes among younger MHD patients.
The authors concluded that total bilirubin could serve as a useful and accessible biomarker for risk stratification in maintenance hemodialysis. They recommended future prospective studies to validate these findings and to determine whether monitoring bilirubin trends could support clinical decision-making or early intervention strategies. Because bilirubin measurement is already part of standard biochemical testing, integrating it into mortality risk assessments may be practical and immediately applicable across dialysis centers.
Reference:
Zhao, Y., Liu, F., Chen, H., & Wu, X. (2025). Total bilirubin as a predictor of all-cause mortality in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. BMC Nephrology. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-025-04621-2
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


