- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Age-Associated Hearing Loss and Peripheral Neuropathy Linked to Higher Mortality in Elderly: Study
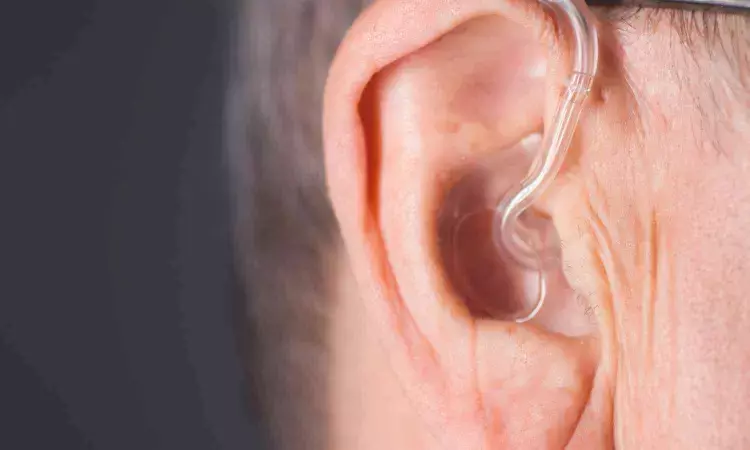
A recent study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society revealed that age-associated hearing loss (AAHL) and peripheral neuropathy (PN) significantly contribute to balance impairment, increased risk of falls, and ultimately, earlier mortality in older adults. This research was a part of the Oklahoma Longitudinal Assessment of the Health Outcomes of Mature Adults (OKLAHOMA) Studies and highlighted the importance of recognizing and addressing these conditions in primary care settings to improve the health and longevity of the elderly population.
The study analyzed data from a total 793 primary care patients by focusing on the prevalence and severity of AAHL, and its association with PN, balance, gait, and mortality. The results found that 63% of participants had some form of AAHL, with a marked 20% expressing low-frequency hearing loss and 4% having unilateral deficits. Additionally, 32% of the participants were diagnosed with PN.
One of the significant outcomes of this study was the clear connection between AAHL, PN, and impaired balance. The participants with moderate to severe AAHL and the individuals with PN showed markedly reduced balance and increased gait time that leads to a higher risk of falls. These factors collectively contributed to a decrease in survival time.
In terms of mortality, the outcomes suggest that both AAHL and PN independently increased the risk of premature death. The participants with moderate or severe AAHL had a 36% higher risk of earlier mortality, while the participants with PN had a 32% higher risk when compared to the participants without these conditions. When both conditions were present, the risk of earlier mortality increased even further by indicating an additive effect.
The structural equation modeling (SEM) suggested that the impact of AAHL and PN on mortality is mediated partly through impaired balance. The mechanisms underlying these associations are likely complex and multifaceted by involving factors such as sensory deficits, reduced mobility, and an increased likelihood of falls.
These findings bring out the critical need for healthcare providers to screen for and address hearing loss and peripheral neuropathy in older adults. Early identification and intervention could reduce the risk of falls and other complications by potentially improving balance, mobility, and overall survival. Overall, the study highlights the significant role that AAHL and PN play in the health outcomes of older adults. As these conditions are common in the aging population, their early detection and management are crucial for enhancing quality of life and extending longevity.
Source:
Mold, J. W., Lawler, F. H., Liao, X., & Bard, D. E. (2024). Associations between hearing loss, peripheral neuropathy, balance, and survival in older primary care patients. In Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.19142
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


