- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Atherosclerosis not Embolism main cause of deep embolic stroke of undetermined source
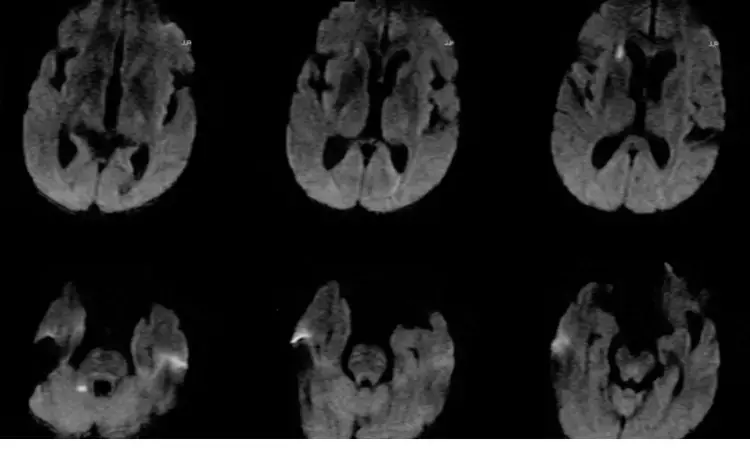
China: Atherosclerosis, not embolism, might be the principal reason for a deep embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS), a recent study in JAHA (Journal of the American Heart Association) has revealed.
The study provided the first high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence that deep embolic stroke of an undetermined source and cortical with/without deep ESUS should be two distinct entities.
The concept of embolic stroke of the undetermined source was proposed to capture a specific stroke subtype needing more extensive workup to lead future clinical trials. Considering the variations in the potential sources or origin of embolic stroke of undetermined origin, Hui‐Sheng Chen, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, China, and colleagues aimed to examine the leading cause of deep ESUS by investigating nonstenotic intracranial atherosclerotic plaque.
For this purpose, the researchers retrospectively screened successive patients with unilateral anterior circulation ESUS. The patients with probable embolism from an extracranial artery, such as carotid plaque, aortic arch plaque, and so on, were excluded. Following the exclusion, patients with ESUS were divided into two groups: deep ESUS and cortical with/without deep ESUS.
Patients underwent high‐resolution intracranial MRI to assess the characteristics of nonstenotic intracranial atherosclerotic plaque. The researchers collected biomarkers of atrial cardiopathy (i.e., P‐wave terminal force in lead V1 on ECG, N‐terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT‐proBNP), and left atrial diameter).
The study led to the following findings:
- The authors found 155 patients with ipsilateral nonstenotic intracranial atherosclerotic plaque, with 49.0% deep ESUS and 51.0% cortical with/without deep ESUS.
- The researchers found a more prevalent plaque in the ostia of the perforator and M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery, with a smaller remodeling index plaque burden and less common occurrence of complicated plaque in deep ESUS compared with cortical with/without deep ESUS.
- Higher level of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and a higher prevalence of atrial cardiopathy in cortical with/without deep ESUS than deep ESUS.
- There was a significant enhancement in the discrimination of vulnerable plaque for predicting ESUS after adjusting for or excluding patients with deep ESUS.
"The study provided the first high-resolution MRI evidence supporting the distinct mechanism of deep vs. cortical with/without deep ESUS," the authors wrote in their study. "The main cause of deep ESUS might be atherosclerosis, not embolism."
They conclude, "the results indicate that because of the nonembolic mechanism, deep ESUS should be ruled out from the family of ESUS."
The study found distinct characteristics of intracranial plaque, such as remodeling index and plaque burden, plaque distribution, and atrial cardiopathy in deep vs. cortical with/without deep ESUS.
Reference:
Luo N, Shang ZY, Tao L, Yang BQ, Chen HS. Atherosclerosis as a Potential Cause of Deep Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: A 3T High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Oct 27:e026737. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026737. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36300665.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


