- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bell's palsy linked to increased risk of ischemic stroke, finds study
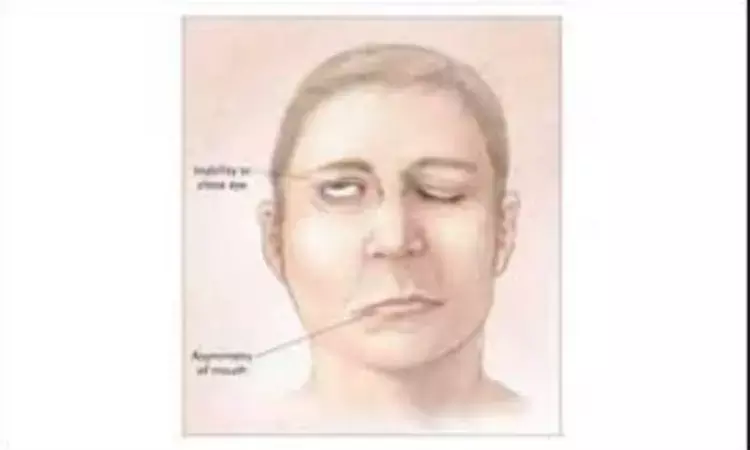
South Korea: Patients with Bell's palsy are at increased risk of ischemic stroke but not of hemorrhagic stroke, suggests a recent study in the journal Auris Nasus Larynx.
Sang-Yeon Lee, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues investigated the association between Bell's palsy and stroke according to the different types of stroke, using a sample cohort based on the national Korean population.
The researchers collected Individuals aged ≥ 20 years from the Korean National Health Insurance Service National Sample Cohort between 2002 and 2013. They then extracted that data for Bell's palsy patients ( n = 3658) and 1:4 matched controls ( n = 14,632). They analyzed the occurrence of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke in both groups. Matching was done on the basis of income, gender, age, and region of residence. For bell's palsy, only those participants were included who received the diagnosis (ICD-10 code, G510) 2 or more times via ambulatory visits for the same episode with steroid treatment. Occurrences of hemorrhagic stroke (I60, I61, and I62) ischemic stroke (I63) were identified using patient admission histories.
Adjusted hazard ratios were calculated using stratified Cox proportional hazard models for the Charlson comorbidity index and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). For the subgroup analyses, we divided the participants by age, sex, and each time period after the onset of Bell's palsy (≤1 year, 1 to 2 years, 2 to 3years, > 3years).
Key findings of the study include:
- The risk of ischemic stroke was significantly increased in Bell's palsy patients compared to that in the controls (adjusted HR = 1.74).
- In the subgroup analyses, a significant association between two clinical disorders was observed in patients aged ≥ 50 years old, regardless of gender.
- The risk of ischemic stroke was significantly increased, especially within 2 years after Bell's palsy.
- In contrast, the risk of hemorrhagic stroke was not significantly increased.
"There is an association of Bell's palsy with ischemic stroke but not with hemorrhagic stroke," concluded the authors.
The study, "Increased risk of ischemic stroke in patients with Bell's palsy: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort," is published in the journal Auris Nasus Larynx.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2020.07.020
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


