- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Genetics based Screening Tool may help predict Gestational Diabetes
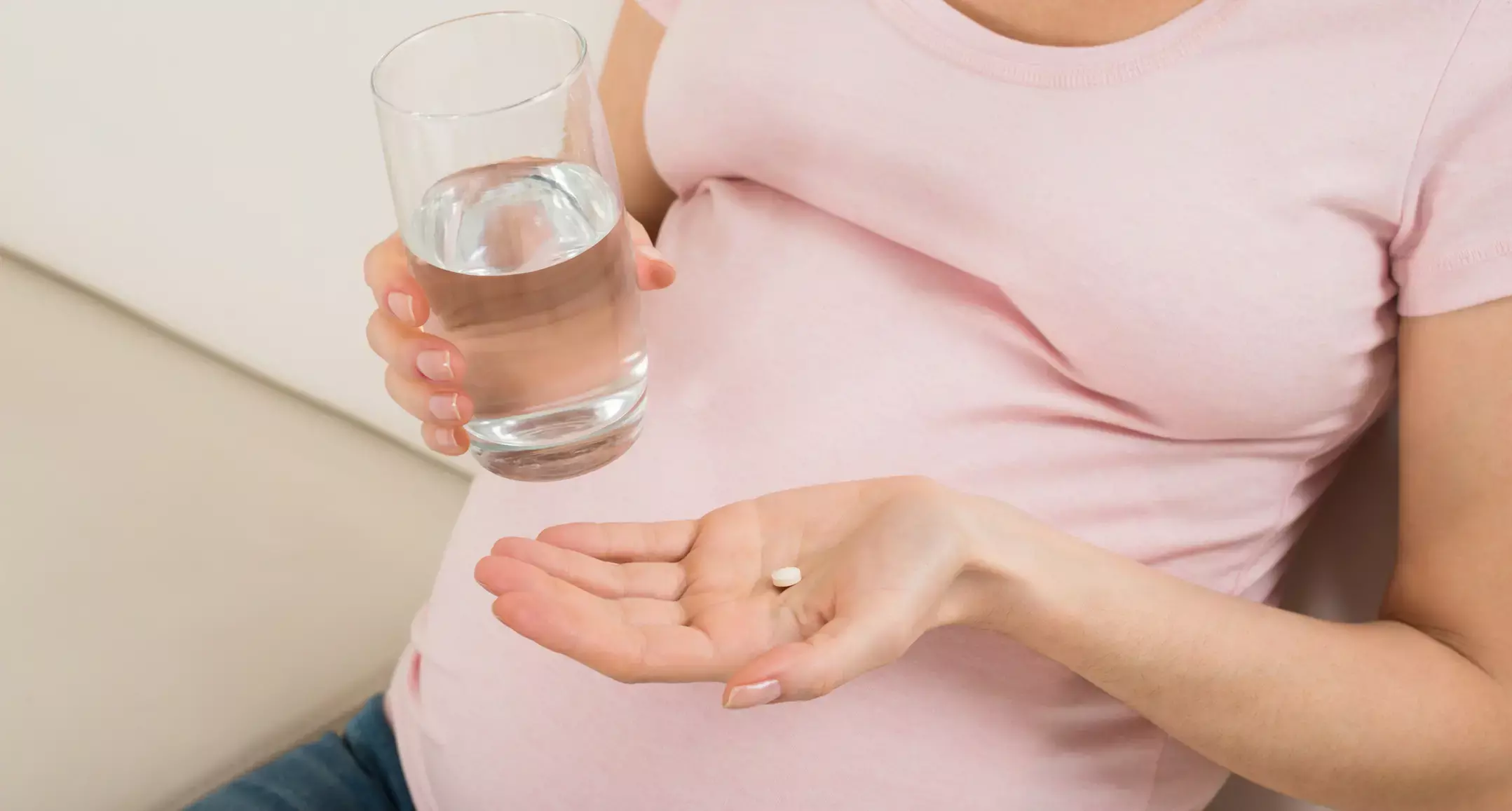

New research found that the Polygenic Risk Score, which is an inexpensive, genetics-based predictive screening tool can be used to identify high-risk women who can develop Gestational Diabetes (GDM) even before conceiving. This can help them to practice GDM preventative preconception lifestyle changes. The study was published in the 'Journal of Personalized Medicine.'
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the most common complication during pregnancy that adversely affects maternal and offspring health. Risk factors such as BMI and age have been associated with increased risks of GDM. But sometimes healthy nulliparous women with no obvious risk factors are also developing GDM. Hence researchers conducted a study to unravel the genetic basis of GDM and investigate relationships between the genetic architecture and genetically constructed risk factors and biomarkers using genetics-based risk scores like the polygenic risk scores (PGS).
For this study, a prospective cohort of 502,637 people aged between 37 and 73 was recruited from the UK Biobank (UKBB). Using detailed questionnaires and clinical assessment all the participants' medical, socio-demographic, lifestyle, environmental, and genetic information was collected. For building the PGS, data from Neale lab GWAS of UKBB phenotype was collected. SNPs were annotated with genes and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using SNPnexus. PGS was derived from a list of relevant SNPs by a machine-learning model. TwoSampleMR package in R was used to run Mendelian Randomization analyses.
Results:
- There were 1270 cases and 13,400 controls from the UKBB for GDM.
- PGS was calculated as a weighted sum of 174 genetic variants.
- To identify women at high risk of GDM, odds ratios were calculated by contrasting the individuals ranked in the top 1%, 2%, 5%, 10%, and 25% PGS values to the individuals whose PGS values are in the lower 50%.
- Higher PGSs were associated with higher incidences of GDM.
- The effect of genetics in the low BMI group was very modest while in medium and high BMI groups the risk of GDM was increased at least linearly with a percentile of PGS.
- Female-specific waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), female-specific adiposity, and predisposition to abdominal fat deposition is the top anthropometric risk factor for GDM.
- MR analyses confirm that genetically proxied levels of glycemic traits such as glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels causatively and substantially increase the odds of GDM.
Thus, the researchers concluded from this study that the polygenic risk score can be used as an early screening tool to identify women at higher risk of GDM even before its onset allowing comprehensive monitoring and preventative programs to mitigate the risks.
For further reading, click here: https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091381
Perišić MM, Vladimir K, Karpov S, Štorga M, Mostashari A, Khanin R. Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022;12(9):1381. doi:10.3390/jpm12091381
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751