- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Increased Risks of Placental Abruption and Preterm Delivery in ART Patients, unravels JAMA study
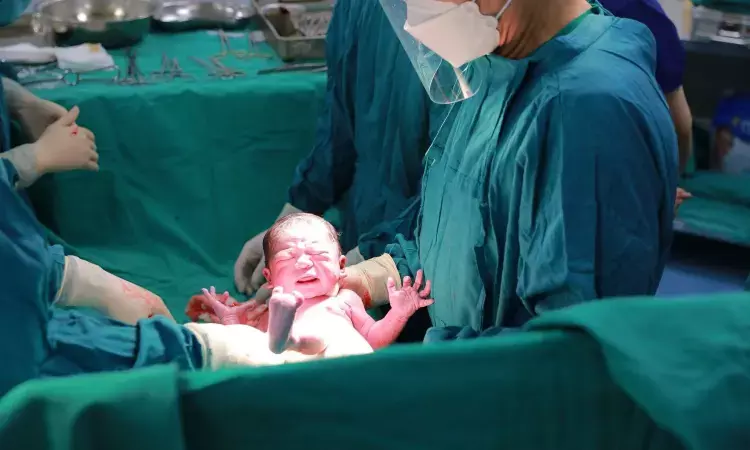
The patients using assisted reproductive technology (ART) may require additional counseling due to the elevated risks of placental abruption and preterm delivery associated with ART. A recent study published in the Journal of American Medical Association unveiled the need for further investigation into the compounded risk of the complications associated with ART pregnancies.
The study assessed the risk of placental abruption in patients who conceived with ART and evaluated whether the combination of placental abruption and ART conception increase the risk of preterm delivery beyond the individual risk associated. This research utilized data from the National Inpatient Sample after encompassing hospital inpatient discharges from over 48 states across the U.S. The participant pool included women from 15 to 54 years who gave birth between 2000 and 2019. The analysis was performed from January to April 2024. The study involved a total of 7,89,01,058 deliveries, with a mean maternal age of 27.9 years. The demographic included 11.7% Black individuals, 18.9% Hispanic individuals, 44.2% White individuals and 25.2% from other races and ethnicities. Also, 98.2% of the deliveries were singleton pregnancies, 68.8% were vaginal deliveries and 52.1% were covered by private insurance.
The risk of placental abruption was found to be higher in ART pregnancies when comparing spontaneous conceptions to ART conceptions. After adjusting for confounders, the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) for placental abruption in ART pregnancies was 1.42, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.34-1.51. This risk was markedly higher in White women when compared Black women.
The likelihood of preterm delivery was also significantly higher in ART pregnancies when compared to spontaneous conceptions, with an AOR of 1.46 (95% CI, 1.42-1.51). Also, the study illuminated a synergistic increase in the risk of preterm delivery when both ART conception and placental abruption were present, with a relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI) of 2.0 (95% CI, 0.5-3.5).
The findings of this study found significant implications for counseling patients who seek infertility treatment. While ART provides a positive path for parenthood in many individuals, it is critical to recognize and address the associated risks. Further research and comprehensive studies are needed to explore the mechanisms behind these risks and to develop inclusive guidelines for managing the pregnancies conceived through ART.
Source:
Zhang, J. T., Lee, R., Sauer, M. V., & Ananth, C. V. (2024). Risks of Placental Abruption and Preterm Delivery in Patients Undergoing Assisted Reproduction. In JAMA Network Open (Vol. 7, Issue 7, p. e2420970). American Medical Association (AMA). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.20970
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


