- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI tools with skull X-rays can help detect meningiomas: Nature study
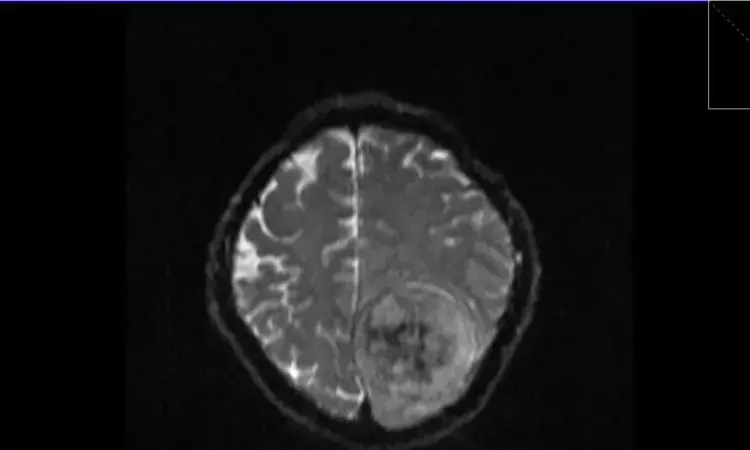
A new study published in the journal of Scientific Reports proposed a potential diagnostic tool by combining deep learning with conventional machine learning approaches, particularly for resource-constrained environments where modern imaging modalities might not be easily accessible.
X-rays are useful for quick screening since they are inexpensive and readily accessible, despite being less detailed than CT or MRI. Deep learning models, especially the convolutional neural networks, can learn minor textural and structural anomalies indicative of meningioma, while classic machine-learning classifiers refine prediction by examining extracted characteristics.
When combined, these methods improve accuracy, lower observer variability, and help physicians detect malignancies early. In neuro-oncology settings, this integrated strategy may strengthen decision-making, increase access to diagnostic assistance, and improve workflow efficiency. Thus, this study was set to investigate the possibility of automated meningioma identification utilizing a widely available and reasonably priced imaging modality.
For this retrospective collection of skull X-ray pictures was taken from St. Vincent's Hospital in South Korea included 158 meningioma patients (632 images) and 201 control participants (804 images) without brain tumors or vascular disorders. The analysis comprised anteroposterior, towne, and lateral views. The core of the deep learning model was EfficientNetB0.
Transfer learning and attention methods were added to improve it. To enhance classification performance, extracted features were included into conventional classifiers like Random Forest and XGBoost. Metrics including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, and AUROC were used to assess the model's performance. Data (824 photos) from Incheon St. Mary's Hospital in South Korea were used for external validation.
The hybrid EfficientNetB0–Random Forest model has the best accuracy (0.97) and AUROC (0.999) in the internal validation cohort. With an accuracy of 0.74 and an AUROC of 0.76, Random Forest performed the best among classifiers, according to external validation data. The model's emphasis on important cranial areas for meningioma identification was emphasized via Grad-CAM displays.
Overall, this work used a hybrid technique that combines deep learning and conventional machine learning classifiers to show the viability and effectiveness of employing skull X-rays for automated meningioma identification. Grad-CAM visualizations reinforced the validity of predictions by offering insights into the model's decision-making process, especially for convexity and parasagittal meningiomas.
Source:
Kim, H. U., Choi, Y., Kim, Y. S., Kim, Y. I., Yoon, W.-S., & Yang, S. H. (2025). Automated meningioma detection using skull X ray images with deep learning and machine learning classifiers. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 40185. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-23933-9
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in


