- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Manganese based nanoparticles may be used to treat cancer
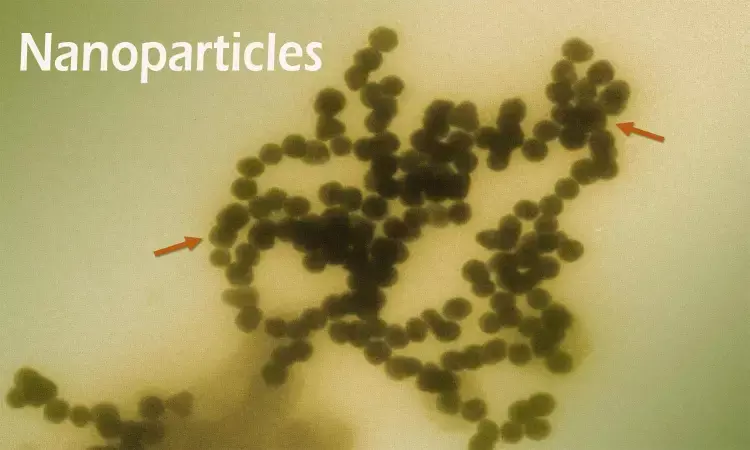
Magnetic fluid hyperthermia is a promising method that can help alleviate the side effects of cancer treatment.
Russia: As treating cancer has become a global goal in the field of medicine, researchers from ITMO University have invented a manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticle that can be used to fight cancer.
Due to their unique magnetic properties, the particles can serve as deactivators of affected cells while having almost no negative impact on healthy tissues. The results have been published in the Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology.
Magnetic fluid hyperthermia is a promising method that can help alleviate the side effects of cancer treatment. This method involves introducing a magnetic nanoparticles-containing sol into a tumour followed by its exposure to a variable magnetic field. This causes the heating of the nanoparticles and leads to the deactivation of cancer cells. But the majority of the materials used for this purpose are toxic to the body and also the particles continue to heat up to relatively high temperatures, which entails serious damage to healthy tissues.
These problems could be solved by the application of a theory in physics which states that the Curie temperature (also known as the Curie point), the temperature at which a sharp decrease in magnetization can be observed.
"When the Curie temperature is reached, ferromagnetic changes into a paramagnetic, consequently the particles cease to be as susceptible to the magnetic field and their further heating stops," explains Vasilii Balanov, a Master's student at ITMO University and one of the research's authors. "When the temperature drops back again, the particles resume their heating. Essentially, we observe a self-management of temperature in a narrow range. If we select a composition that experiences such a transition at the temperature we need, then it could prove effective for magnetic fluid hyperthermia." he added.
Researchers used the particles with the general formula Zn(x)Mn(1-x)Fe2O4, in which zinc and manganese are selected in a certain proportion. They don't have a toxic effect on the body, and with the right ratio of manganese and zinc, Curie temperature in the range of 40-60 degrees Celsius can be achieved. This temperature allows the cancer cells to deactivate, concurrently, the short-term thermal contact is relatively harmless to healthy tissues.
As of now, the scientists have synthesized the nanoparticles and studied their magnetic properties. The experiments confirmed that the material doesn't heat up above 60 degrees Celsius when exposed to a variable magnetic field. Coming next will be the experiments on living cells and, if these are successful, on animals.
For further reading click on the following link,
MBBS
Dr K B AARTHI-has completed MBBS from SRM UNIVERSITY TAMIL NADU,Her interest is in the field of Pediatrics and Anaesthesia, also passionate in doing research and publishing articles.She joined Medical Dialogues in 2020 and publishes health news and medical updates. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751,9786713226
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


