- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Simvastatin a potential candidate drug in ovarian clear cell carcinomas: Oncotarget
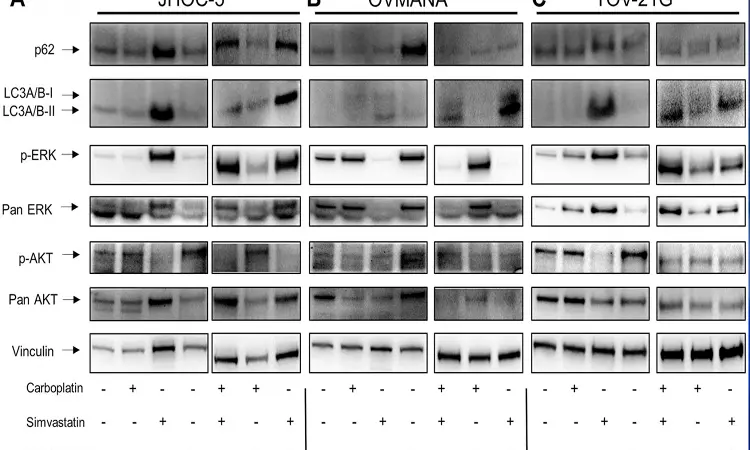
Oncotarget recently published "Simvastatin is a potential candidate drug in ovarian clear cell carcinomas" which reported that based on previous studies, the authors assessed the anti-proliferative effect of simvastatin, a Rho GTPase interfering drug, in three OCCC cell lines: JHOC-5, OVMANA and TOV-21G, and one high-grade serous ovarian cancer cell line, Caov3. The authors used the Rho GTPase interfering drug CID-1067700 as a control.
All OCCC cell lines were more sensitive to single-agent simvastatin than the HGSOC cells, while all cell lines were less sensitive to CID-1067700 than to simvastatin.
Most treatments inhibited migration, while only simvastatin and CID-1067700 also disrupted actin organization in the OCCC cell lines.
Treatments with simvastatin consistently reduced c-Myc protein expression in all OCCC cell lines and displayed evidence of causing both caspase-mediated apoptotic cell death and autophagic response in a cell line dependent manner.
Conclusively, simvastatin efficiently controlled OCCC proliferation and migration, thus showing potential as a candidate drug for the treatment of OCCC.
"Simvastatin efficiently controlled OCCC proliferation and migration, thus showing potential as a candidate drug for the treatment of OCCC.'
Dr. Ingrid Hedenfalk from The Lund University said, "Ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) is a subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) accounting for 5–10% of cases diagnosed in Europe and America, while the incidence in Asia is reported to be higher (10–20%)."
The Oncotarget authors recently reported Rho GTPases and their associated pathways to be differentially expressed between OCCC compared to the other major EOC subtypes.
Rho GTPases have been studied as targets for cancer treatment in various settings due to their role in regulating key cellular functions including the maintenance of cytoskeletal integrity, cell migration and proliferation, but also in metastasis and progressive disease in many cancer types.
However, targeting Rho GTPases directly is challenging due to their high binding affinity for GTP/GDP, and indirect strategies such as targeting the localization of Rho GTPases to the cell membrane are promising alternatives.
CID-1067700 is a pan-GTPase inhibitor that inhibits binding of GTP/GDP and downstream binding of Rho GTPases to their targets and is used as a comparator for Rho GTPase interference as a druggable target in OCCC.
Based on the deregulated expression of both Rho GTPases and cytoskeletal pathways in primary human OCCC tumors in our previous work, they investigated the potential of simvastatin, a lipophilic statin, as a targeted treatment in OCCC cell lines with CID-1067700 as a comparator in the present study.
The Hedenfalk Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper that while HGSOC has been studied intensively, OCCC remains a rare subtype with poor prognosis, but this study, although investigative, demonstrates a potential for simvastatin treatment in OCCC.
Simvastatin could act through Rho GTPase interference as simvastatin affects the cytoskeletal integrity of OCCC cells at levels which can be achieved in plasma.
However, the mechanism is different from Rho GTPase inhibition by CID-1067700.
Furthermore, caution should be given, as this data suggest that a combination with standard chemotherapy may elicit an antagonistic response.
Whether this is of clinical relevance for patients receiving statin treatment remains unclear and needs to be investigated further, but simvastatin holds promise as a potential drug candidate in OCCC and warrants further investigation in the clinical setting.
For further reference log on to:
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


