- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Allopurinol lowers risk of macular edema among diabetes patients
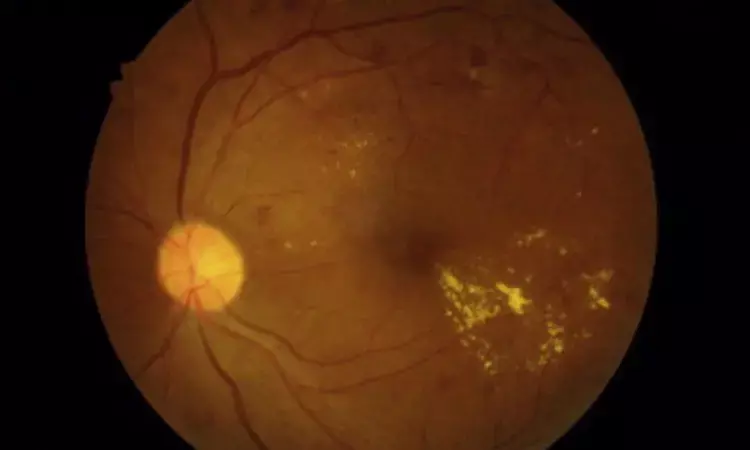
USA: A recent study published in Ocular Immunology and Inflammation has shown that allopurinol could reduce the risk of diabetic macular edema (DME). DME is one of the major causes of visual loss among patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetic eye disease is a leading cause of vision loss in people aged 20 to 74. It can affect central vision and lead to vision decline ranging from vision blurring to blindness, which can substantially impact the quality of life and independence. Of the visually disabling conditions in patients with diabetic eye disease, DME left untreated, is a frequent cause of vision loss.
For the treatment of macular edema, focal/grid laser photocoagulation has been the standard of care since the 1980s and until 2010. The treatment increases the possibility of vision gain and reduces the risk of vision loss compared with no treatment. Recent phase II and III trials with aflibercept and ranibizumab and phase II trials with bevacizumab, intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents have been revealed to be superior to focal/grid laser for decreasing the risk of vision loss and increasing the possibility of vision gain.
Allopurinol may limit the inflammation-driving diabetic macular edema by inhibiting xanthine oxidase, a subsequent release of inflammatory cytokine leading to the breakdown of the blood–retina barrier.
Considering the above, S. Scott Sutton from the University of South Carolina in Columbia, South Carolina, USA, and colleagues aimed to examine the relationship between allopurinol and diabetic macular edema among type 2 diabetic United States veterans using a retrospective cohort study. For estimating the risk of diabetic macular edema, propensity score matching and Cox hazard models were used.
Propensity score-matched Cox models showed that allopurinol was associated with a 24.6% reduction in the risk of DME (HR = 0.754).
The researchers wrote, "among patients with diabetes mellitus, allopurinol could reduce the risk of diabetic macular edema."
"Further research is warranted into the effects of allopurinol on DME," they concluded.
Reference:
The study, "Allopurinol and the Risk of Diabetic Macular Edema among US Veterans with Type 2 Diabetes," was published in the journal Ocular Immunology and Inflammation. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09273948.2023.2170886
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


