- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Baseline Risk Factors Linked to Chronic Hypotony After Tube Shunt Surgery,: Study
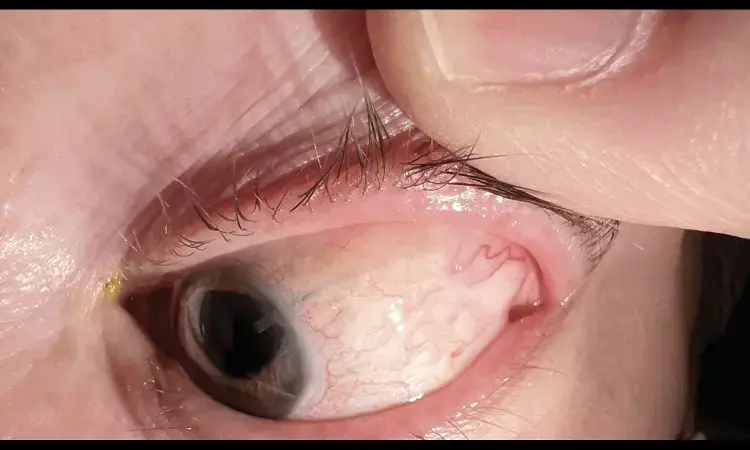
Researchers have found in largest prospective dataset on tube shunt outcomes that Chronic hypotony is a rare complication of tube shunt surgery that often leads to reduced visual acuity and the key baseline risk factors include Baerveldt implant use, uveitic glaucoma, and poor initial vision..
The study was performed to describe the incidence and risk factors for chronic hypotony following tube shunt surgery. It consisted of a pooled analysis of three independent, multicenter randomised clinical trials. There were 621 patients with medically uncontrolled glaucoma, including 276 from the Ahmed Baerveldt Comparison Study, 238 from the Ahmed Versus Baerveldt Study, and 107 from the tube group of the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy Study. Enrolled patients had been randomised to placement of either an Ahmed glaucoma valve (model FP7) or a Baerveldt glaucoma implant (model 101-350). Baseline and follow-up data were obtained on a per-patient level and pooled. The associations between baseline risk factors and chronic hypotony were explored using a Cox proportional hazards regression model. The main outcome was chronic hypotony, defined as intraocular pressure (IOP) ≤ 5 mmHg on 2 consecutive visits after 3 months, tube ligation, or implant removal for hypotony.
Results: The cumulative probability of chronic hypotony after tube shunt surgery was 4.1% (95% CI = 2.6% to 6.1%) at 5 years. Reduction in visual acuity (VA) from baseline was observed in 15 patients (71%) at the time of hypotony diagnosis. Significant predictors of chronic hypotony in multivariable analysis included randomized treatment (for Baerveldt glaucoma implant; HR = 5.12; 95% CI = 1.51 to 17.43; P = 0.009), uveitic glaucoma (HR = 3.75; 95% CI = 1.26 to 11.15; P = 0.017), and preoperative visual acuity (per logMAR unit increase; HR = 1.55; 95% CI = 1.04 to 2.32; P = 0.031).
Chronic hypotony is an uncommon complication of tube shunt surgery that usually produces a reduction in visual acuity. Baseline factors associated with this complication are Baerveldt implantation, uveitic glaucoma, and poor visual acuity. This study analyzes the largest prospectively collected dataset to date on tube shunt surgery.
Reference:
Chronic Hypotony After Tube Shunt Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Data from Three Randomized Clinical Trials. Gedde, Andrew Y. et al. American Journal of Ophthalmology, Volume 0, Issue 0
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


