- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Calcium channel blockers represent an important risk factor for glaucoma
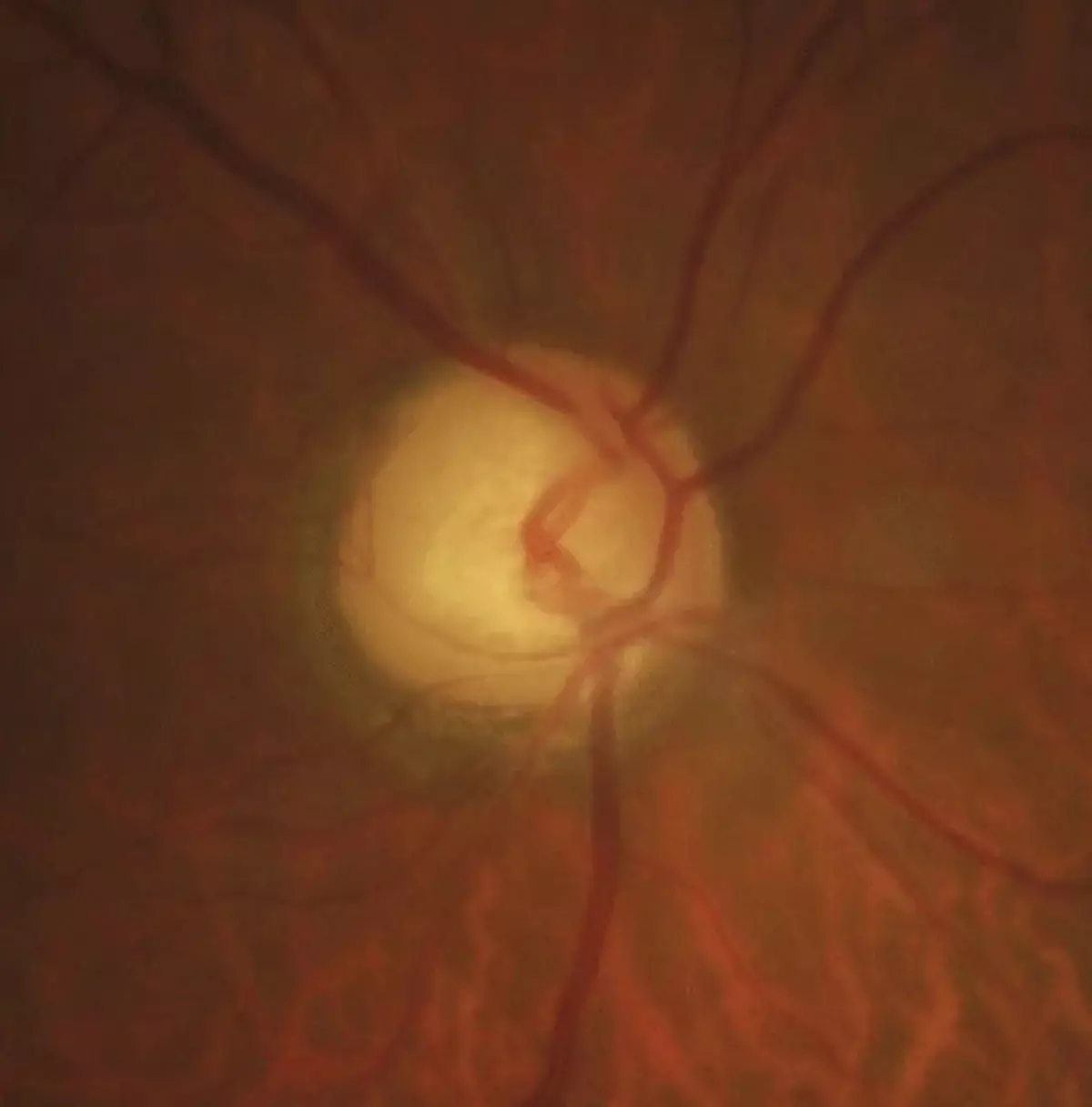
Calcium channel blocker (CCB) use has been associated with an increased risk of glaucoma in exploratory studies. To examine the association of systemic CCB use with glaucoma and related traits among UK Biobank participants, a population-based cross-sectional study carried out by Kastner A et al included UK Biobank participants with complete data (2006-2010) for analysis of glaucoma status, intraocular pressure (IOP), and optical coherence tomography (OCT)–derived inner retinal layer thicknesses. Data analysis was conducted in January 2023.
Calcium channel blocker use was assessed in a baseline touchscreen questionnaire and confirmed during an interview led by a trained nurse. The primary outcome measures included glaucoma status, corneal-compensated IOP, and 2 OCT-derived inner retinal thickness parameters (macular retinal nerve fiber layer [mRNFL] and macular ganglion cell–inner plexiform layer [mGCIPL] thicknesses). Authors performed logistic regression and linear regression analyses to test for associations with glaucoma status and IOP and OCT-derived inner retinal thickness parameters, respectively.
This study included 4,27,480 adults. Their median age was 58 (IQR, 50-63) years, and more than half (54.1%) were women. There were 33 175 CCB users (7.8%). Participants who had complete data for glaucoma status (n = 427 480), IOP (n = 97 100), and OCT-derived inner retinal layer thicknesses (n = 41 023) were eligible for respective analyses. After adjustment for key sociodemographic, medical, anthropometric, and lifestyle factors, use of CCBs (but not other antihypertensive agents) was associated with greater odds of glaucoma (odds ratio [OR], 1.39 [95% CI, 1.14 to 1.69]; P = .001). Calcium channel blocker use was also associated with thinner mGCIPL (−0.34 μm [95% CI, −0.54 to −0.15 μm]; P = .001) and mRNFL (−0.16 μm [95% CI, −0.30 to −0.02 μm]; P = .03) thicknesses but not IOP (−0.01 mm Hg [95% CI, −0.09 to 0.07 mm Hg]; P = .84).
In this study, an adverse association between CCB use and glaucoma was observed, with CCB users having, on average, 39% higher odds of glaucoma. Calcium channel blocker use was also associated with thinner mGCIPL and mRNFL thicknesses, providing a structural basis that supports the association with glaucoma. The lack of association of CCB use with IOP suggests that an IOP-independent mechanism of glaucomatous neurodegeneration may be involved. Although a causal relationship has not been established, CCB replacement or withdrawal may be considered should glaucoma progress despite optimal care.
Source: Kastner A, Stuart KV, Montesano G, et al. Calcium Channel Blocker Use and Associated Glaucoma and Related Traits Among UK Biobank Participants. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online September 07, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.3877
Dr Ishan Kataria has done his MBBS from Medical College Bijapur and MS in Ophthalmology from Dr Vasant Rao Pawar Medical College, Nasik. Post completing MD, he pursuid Anterior Segment Fellowship from Sankara Eye Hospital and worked as a competent phaco and anterior segment consultant surgeon in a trust hospital in Bathinda for 2 years.He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Vitreo-Retina at Dr Sohan Singh Eye hospital Amritsar and is actively involved in various research activities under the guidance of the faculty.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


