- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Cataract surgery and iStent Inject combo tied to significantly greater reduction of IOP in mild glaucoma patients: Study
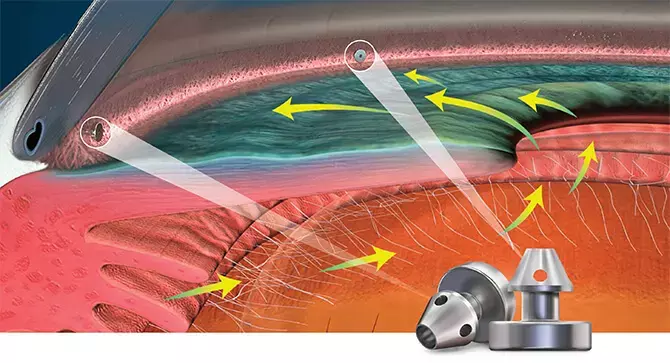
Cataract surgery and iStent Inject combo tied to significantly greater reduction of IOP in mild glaucoma patients suggests a study published in the Ophthalmology Glaucoma.
A study was done to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combined cataract surgery with insertion of an ab interno trabecular micro bypass device (iStent Inject, Glaukos Corporation) compared to cataract surgery alone in patients with mild-to-moderate glaucoma. Eyes with visually-significant cataracts and mild-to-moderate glaucoma with preoperative intraocular pressure (IOP) of 12 – 30 mmHg on 0 to 3 ocular hypotensive medications. Participants' eyes were randomised (2017-2020) 1:1 to combine cataract surgery with iStent Inject (treatment group, n=56) or cataract surgery alone (control group, n=48), and followed up for two years. The co-primary effectiveness endpoints were the number of ocular hypotensive medications and IOP at 24 months post-surgery. The secondary effectiveness endpoints were ocular comfort as measured by the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) and vision-related quality of life as measured by the Glaucoma Activity Limitation Questionnaire (GAL-9) at 24 months. Safety measures included postoperative visual acuity, any unplanned return to the operating theatre, adverse events, and complications.
Results: Participants (67.3% male) were aged 53-85 years and treatment groups were similar in terms of mean medicated IOP (treatment group 17.7 mmHg ± 4.0; control group 17.1 mmHg ± 3.1), and number of ocular hypotensive medications (treatment group 1.69 ± 1.05; control group 1.80 ± 1.22) at baseline. At 24 months, the number of ocular hypotensive medications were 0.7 ± 0.9 in the treatment groups compared to 1.5 ± 1.9 in the control group, with an adjusted difference of 0.6 fewer medications per eye in the treatment group (95% CI 0.2 to 1.1, p=0.008). 57% of eyes in the treatment group were on no glaucoma medications compared to 36% in the control group. There was no significant difference in IOP between the two groups beyond the 4-weeks. There were no differences in patient-reported outcomes between the two groups. The visual outcomes and safety profiles were similar between the two groups. Combined cataract surgery with iStent Inject achieved a clinically- and statistically significantly greater reduction in ocular hypotensive medication usage at 24 months compared to cataract surgery alone, with no significant difference in IOP.
Reference:
Jennifer C. Fan Gaskin, Deus Bigirimana, George Yu Xiang Kong, Myra B. McGuinness, Alp Atik, Lei Liu, Anne MV. Brooks, Ghee Soon Ang. Prospective, Randomised Controlled Trial of Cataract Surgery versus combined Cataract Surgery with insertion of iStent Inject, Ophthalmology Glaucoma, 2024, ISSN 2589-4196, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogla.2024.02.004.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589419624000310)
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


