- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Carbon dioxide Laser Excision: A Promising Minimally Invasive Treatment for Large Xanthelasma Palpebrarum, Study Finds
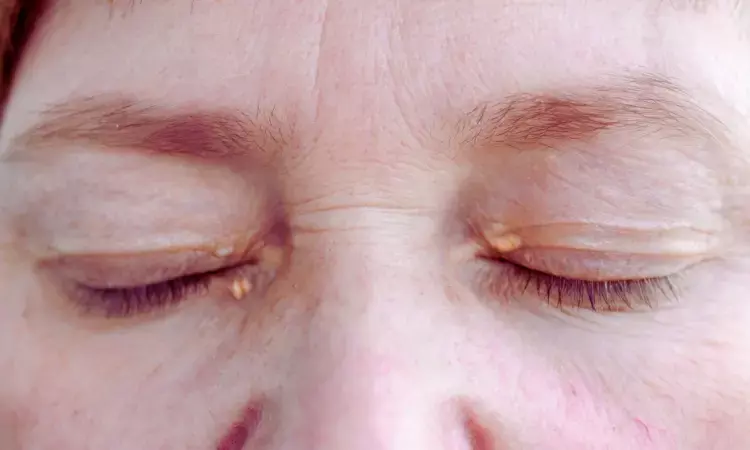
China: A recent study published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology highlights the effectiveness of carbon dioxide laser excision as an advanced treatment option for large xanthelasma palpebrarum, offering a precise and minimally invasive approach. The study revealed that CO₂ laser excision is highly effective in treating xanthelasma palpebrarum, achieving clearance rates exceeding 99% for mild to moderate lesions and 95% for severe cases.
"Recurrence occurred in 6.8% of patients, with higher rates observed in lesions larger than 2 mm. Minor complications included scarring (4.4%), hyperpigmentation (8.1%), and hypopigmentation (8.5%), reinforcing its potential as a reliable treatment option," the researchers reported.
Xanthelasma palpebrarum is a common lipid disorder characterized by yellowish plaques on the eyelids. While generally benign, these lesions can be cosmetically distressing and may indicate underlying lipid abnormalities. Traditional treatment methods include surgical excision, chemical peeling, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, each with its own limitations, such as scarring, pigmentation changes, and recurrence.
Against the above background, Dingqiao Wang, Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases, Guangzhou, China, and colleagues aimed to assess the long-term effectiveness and safety of CO₂ laser excision as an innovative approach for treating large xanthelasma palpebrarum.
For this purpose, the researchers included 295 patients diagnosed with xanthelasma palpebrarum, categorizing them into 246 with grade I, 16 with grade II, 22 with grade III, and 11 with grade IV lesions. All patients underwent CO₂ laser excision and were monitored for 12 months. Treatment efficacy was determined based on clearance and recurrence rates, assessed through digital photography, while complications were documented.
Key Findings:
- The study included 66 male and 229 female participants, with an average age of 41.7±11.6 years.
- Clearance rates were over 99% for grades I-III and approximately 95% for grade IV lesions.
- The overall recurrence rate was 6.8%, with significantly higher recurrence in lesions over 2 mm in height than those under 2 mm.
- Complications during the 12-month follow-up included scarring (4.4%), hyperpigmentation (8.1%), and hypopigmentation (8.5%), with no severe adverse events reported.
The researchers highlight CO₂ laser excision as a precise, minimally invasive, and effective treatment for large xanthelasma palpebrarum lesions, marking a significant advancement in therapeutic approaches. Their findings demonstrate high efficacy, particularly for extensive lesions, with clearance rates exceeding 95%, a low recurrence rate of 6.8%, and minimal complications such as scarring, hyperpigmentation, and hypopigmentation.
"By employing laser technology for precise excision, this method presents notable advantages over conventional treatments. However, we acknowledge limitations, including the study’s single-centre, retrospective design and follow-up duration, necessitating future multicentre trials to validate these findings and refine treatment protocols," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Wang D, Mao Z, Li Z, Gao W, Qu Y, Li X, Jiang Y, Lin X. Carbon dioxide laser excision as a novel treatment for large xanthelasma palpebrarum: long-term efficacy and safety. Br J Ophthalmol. 2025 Feb 24;109(3):427-432. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2024-325581. PMID: 39237290.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


