- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Handheld chromatic pupillometry can accurately and rapidly reveal functional loss in glaucoma
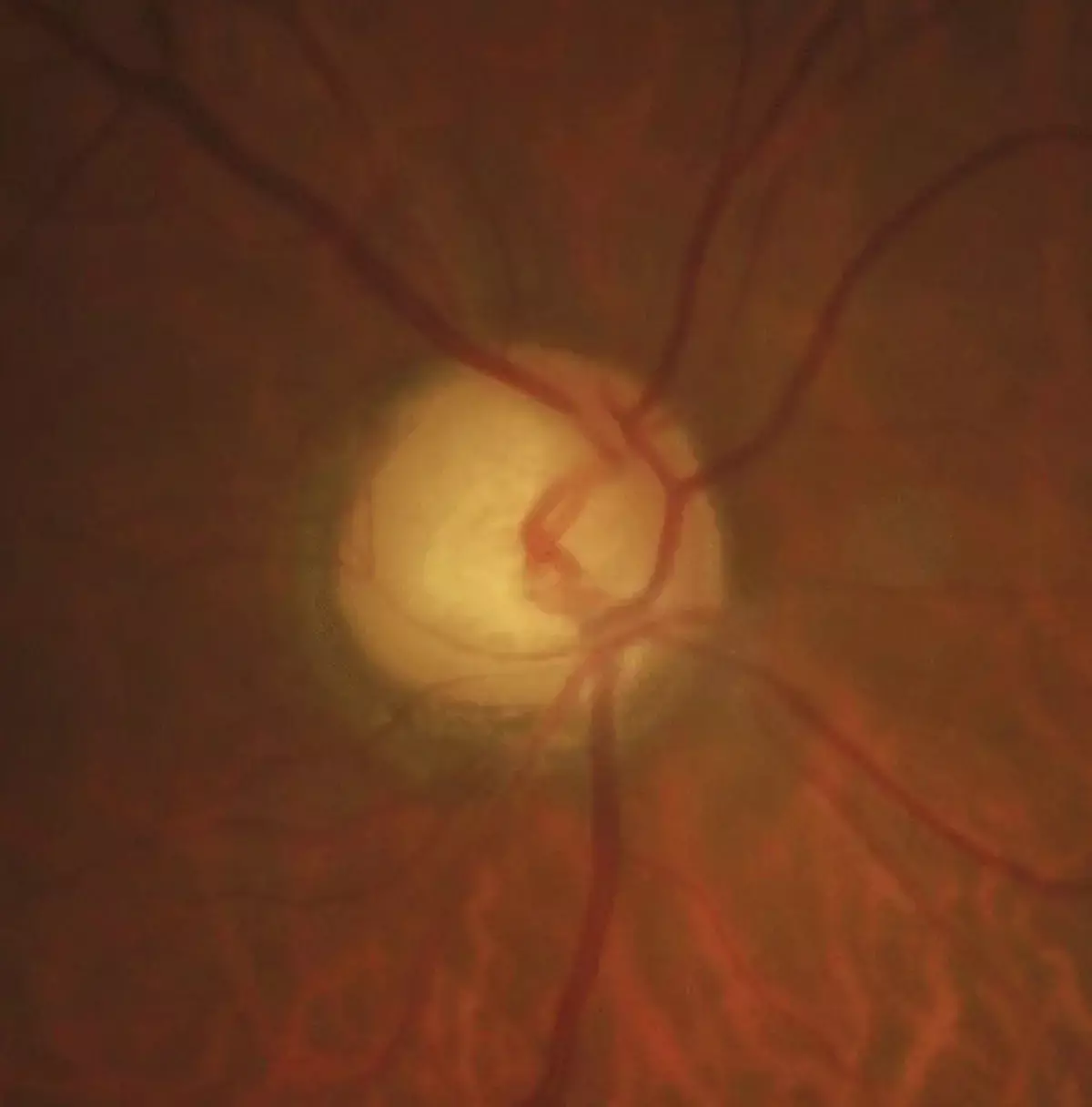
Handheld chromatic pupillometry can accurately and rapidly reveal functional loss in glaucoma, suggests a new study published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology.
Early detection and treatment of glaucoma can delay vision loss. In this study, we evaluate the performance of handheld chromatic pupillometry (HCP) for the objective and rapid detection of functional loss in glaucoma.
In this clinic-based, prospective study, we enrolled 149 patients (median (IQR) years: 68.5 (13.6) years) with confirmed glaucoma and 173 healthy controls (55.2 (26.7) years). Changes in pupil size in response to 9 s of exponentially increasing blue (469 nm) and red (640 nm) light-stimuli were assessed monocularly using a custom-built handheld pupillometer. Pupillometric features were extracted from individual traces and compared between groups. Features with the highest classification potential, selected using a gradient boosting machine technique, were incorporated into a generalised linear model for glaucoma classification. Receiver operating characteristic curve analyses (ROC) were used to compare the performance of HCP, optical coherence tomography (OCT) and Humphrey Visual Field (HVF).
Results
Pupillary light responses were altered in glaucoma compared with controls. For glaucoma classification, Handheld chromatic pupillometry yielded an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.94, a sensitivity of 87.9% and specificity of 88.4%.
The classification performance of HCP in early-moderate glaucoma was similar to HVF (AUC=0.91) and reduced compared with optical coherence tomography (OCT).
For severe glaucoma (VFMD ≤ -12 dB), Handheld chromatic pupillometry had an excellent classification performance that was similar to HVF and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Handheld chromatic pupillometry allows for an accurate, objective and rapid detection of functional loss in glaucomatous eyes of different severities.
Reference:
Najjar RP, Rukmini AV, Finkelstein MT, et alHandheld chromatic pupillometry can accurately and rapidly reveal functional loss in glaucoma, British Journal of Ophthalmology 2023;107:663-670.
Keywords:
Handheld, chromatic pupillometry, accurately, rapidly, reveal, functional, loss, glaucoma, British Journal of Ophthalmology, Najjar RP, Rukmini AV, Finkelstein MT
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


