- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Multi-Ingredient Supplement Shows Promising Results for Dry Eye Disease in Clinical Trial
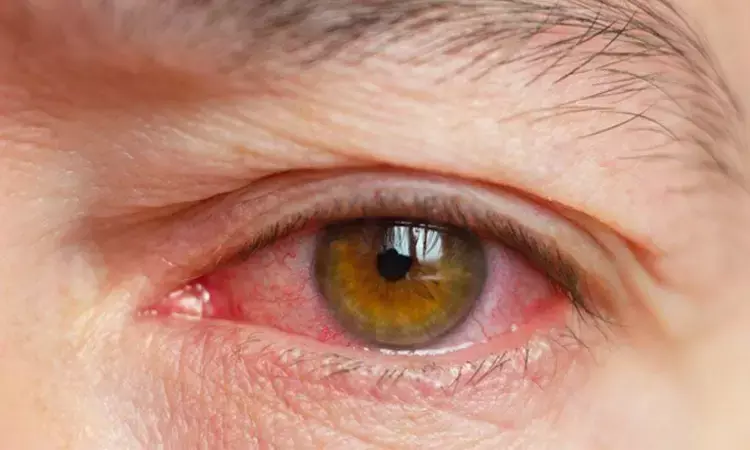
USA: Dry eye disease (DED) affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort and impairing vision quality. However, a glimmer of hope emerges from the latest research findings published in the Frontiers in Ophthalmology. A novel multi-ingredient supplement has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in alleviating ocular symptoms and improving tear production among patients with DED, according to results from a rigorous randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
The study showed that a novel nutritional supplement of lutein, zeaxanthin isomers, curcumin, and vitamin D3 (LCD) demonstrated therapeutic potential as a once-daily treatment for patients with dry eye disease.
"Once-daily LCD supplementation significantly improved tear production, quality and stability, improved participants’ symptoms, and reduced ocular surface damage and inflammation," the researchers reported. They suggested that LCD supplementation could offer a useful adjunct to artificial tears for patients with DED.
The multi-ingredient supplement is formulated with a synergistic blend of nutrients and compounds that support ocular health, including omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and essential vitamins. This unique combination targets multiple pathways involved in DED pathogenesis, providing comprehensive relief from symptoms and promoting long-term eye health.
While artificial tears are the traditional mainstay of treatment for DED, addressing the underlying pathophysiology could relieve symptoms and prevent progression. Considering this, Neda Gioia, Integrative Vision Corp, Shrewsbury, NJ, United States, and colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of a proprietary blend of lutein, zeaxanthin isomers, curcumin, and vitamin D3 as a daily supplement in adult participants with DED.
The study Participants were randomized to receive one LCD supplement capsule (zeaxanthin isomers 4 mg, lutein 20 mg, curcumin 200 mg curcuminoids, and vitamin D3 600 IU) or placebo per day for eight weeks (LCD, n=77; placebo, n=78). Primary outcomes were changes in ocular symptoms (Ocular Surface Disease Index [OSDI] and tear volume (Schirmer’s test).
The following were the study’s key findings:
- The study met its primary endpoints: the LCD group demonstrated significantly better Schirmer’s test scores, and improvement in overall OSDI score, versus placebo, at Day 56.
- Scores for total OSDI, and symptoms and vision domains, significantly improved by Day 14 for LCD versus placebo, and were maintained to Day 56.
- In addition, the LCD group demonstrated significantly improved tear film break-up time (TBUT) and tear film osmolarity, versus placebo, by Day 56, along with significant improvements in corneal and conjunctival staining, and inflammation (matrix metalloproteinase-9).
- Total Standard Patient Evaluation of Eye Dryness (SPEED) score, and scores for the frequency and severity domains were significantly improved by Day 14 for LCD versus placebo and maintained to Day 56.
- There was no difference between groups for artificial tear usage. The supplement was well-tolerated.
In conclusion, the trial highlights the benefits to patients with DED of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant nutritional support with this proprietary supplement by addressing the characteristic loss of tear homeostasis, improving their experience of symptoms, and ameliorating the ocular inflammation and damage that are the basis of DED pathophysiology.
Reference:
Gioia N, Gerson J, Ryan R, Barbour K, Poteet J, Jennings B, Sharp M, Lowery R, Wilson J, Morde A, Rai D, Padigaru M and Periman LM (2024) A novel multi-ingredient supplement significantly improves ocular symptom severity and tear production in patients with dry eye disease: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Front. Ophthalmol. 4:1362113. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1362113
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


