- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
New Study Finds Possible Link Between endophthalmitis and COVID-19
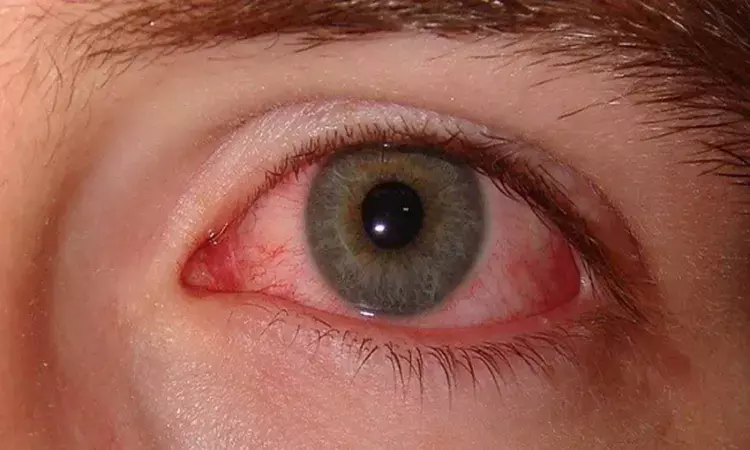
Researchers are warning of a possible link between a rare and devastating eye infection and COVID-19.They have observed that air jets from the superior edge of the mask radiate toward the eyes, contaminating the surgical field. Consequently patients wearing face masks during intravitreal injections may be at a higher risk of endophthalmitis, according to a study.
In just two months, three patients at New York's Northwell Health hospital were diagnosed with keratitis that quickly led to endophthalmitis and profound vision loss. One patient's eye had to be removed. All three patients tested positive for COVID-19. Results of the retrospective review were released this month at AAO 2020 Virtual, the 124th annual meeting of the American Academy of Ophthalmology. The researchers hope their findings will encourage the medical community to consider the eye when evaluating the role of anti-infectious treatment and immunomodulation.
While the evidence does not show that the virus caused the devastating eye infections, the occurrence of keratitis leading to rapid perforation and endophthalmitis is exceedingly rare. To have three cases present over the course of two months in New York, a coronavirus epicenter, is a cause for more investigation, researchers say.
Keratitis is an infected sore on the eye. In rare instances, keratitis can lead to endophthalmitis, an inflammation of fluids inside the eye, usually due to infection caused by various bacteria and fungi. Typically, it's associated with surgery or trauma. Endophthalmitis can cause significant vision loss, including blindness. In some cases, the eye must be removed. Symptoms typically appear rapidly and include pain, red eye, discharge from the eye, lid swelling and reduced vision.
Ophthalmologist Amilia Schrier, MD, reports that the three patients, all in their 60s, and hailing from Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Long Island, presented to the Northwell Health Ophthalmology Department within the same two-month period. Two were outpatients and one was in the hospital at the time of keratitis diagnosis. All three tested positive for the coronavirus. One of the outpatients was later admitted to the hospital and died. Each patient had a different organism on culture: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Serratia marcescens, and Candida parapsilosis.
"The incidence of keratitis progressing to endophthalmitis is extremely low," Dr. Schrier said. "A 2012 study reported only 27 out of 9,934 eyes in a 15-year period experienced endophthalmitis caused by keratitis.1
Dr. Schrier continued, "three of these cases in a two-month period with COVID-19 positivity suggests that there may be an association between COVID-19 infection and severe eye disease."
"While these findings do require further research, caution must be undertaken when interpreting these results," said Sonal S. Tuli, MD, a clinical spokesperson for the Academy who was not involved in the study. "The findings do not suggest that COVID-19 causes endophthalmitis but that there is some relationship between the two. It is possible that some aspect of the health of these individuals made them more liable to get infected with COVID-19 as well as a severe infection in their eye such as a poor immune system or nutritional deficiencies. It is also possible that these findings are incidental because of the large numbers of COVID positive patients presenting to New York hospitals during the peak of the pandemic in New York.
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


