- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Oral doxycycline proves efficacious in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy: JAMA
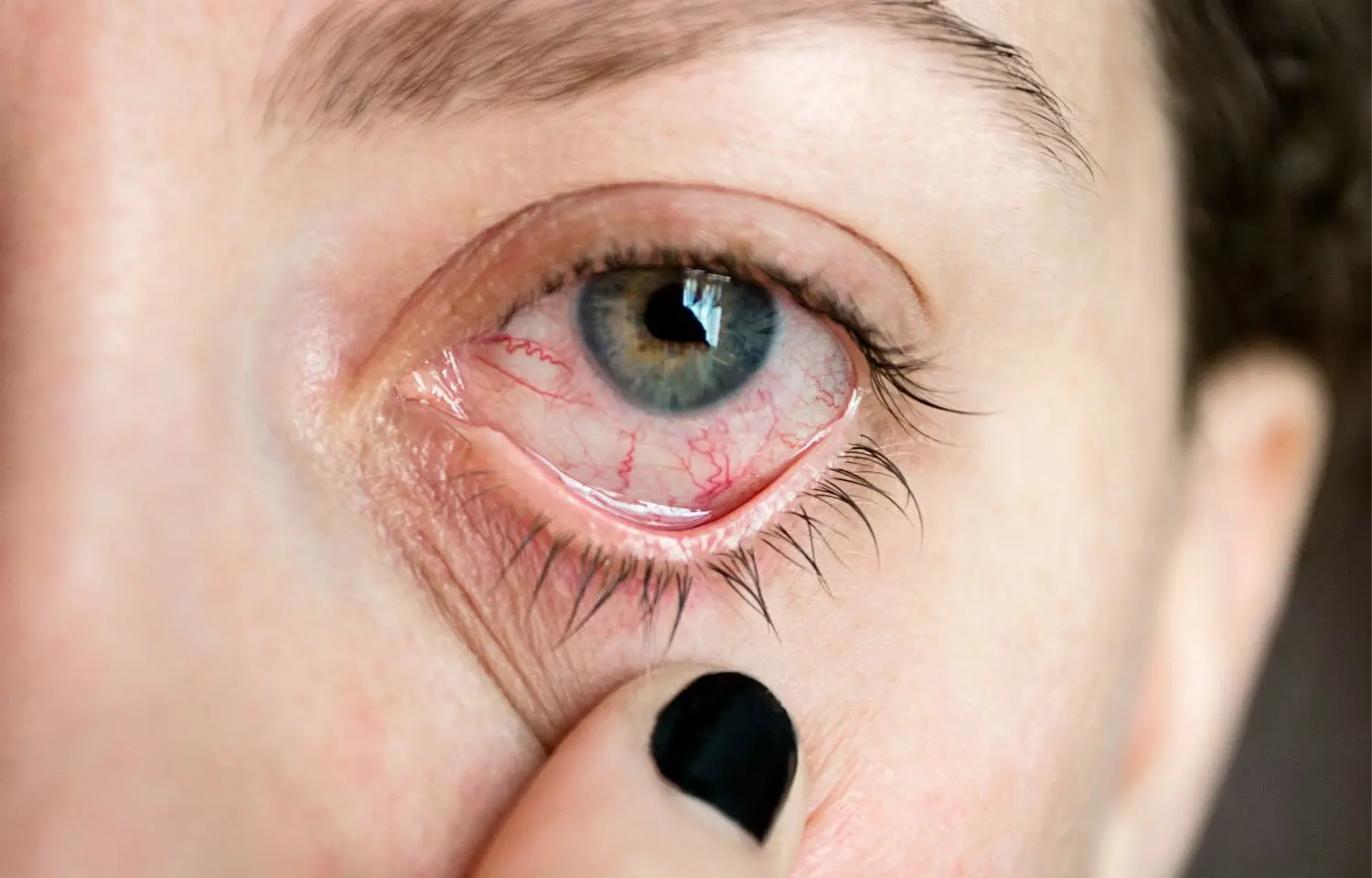
CHINA: In a recent study released in JAMA Ophthalmology, it was reported that patients with mild TAO who took oral doxycycline 50 mg once a day saw higher relief from TAO-related symptoms after 12 weeks compared to those who took a placebo.
Although thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy is an autoimmune disorder, the exact cause of the condition is unknown. The quality of life is significantly impacted by mild thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO), however there are no clinical recommendations for treatment. For the patient with mild TAO, waiting it out is the best course of action. In addition to its antibacterial activities, doxycycline exhibits a potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effect. Doxycycline can be used to treat mild TAO, according to the available research.
The researchers intended to assess doxycycline's short-term (12 weeks) effectiveness in treating mild TAO.
For this purpose, 148 patients had their eligibility for this placebo-controlled, multicenter, randomized, double-masked trial evaluated. Following exclusions, 100 patients with mild TAO (mildly impacted orbicular soft tissue) at 5 locations in China were enrolled and followed up with for 12 weeks. A total of 75 participants (75.0%) were female, and 100 (100.0%) were Asian. The mean (SD) age was 36.7 (9.1) years. Participants' medication compliance was examined by interviews and a count of extra tablets. For 12 weeks, participants were randomized to receive either doxycycline (50 mg) or a placebo. 50 subjects were given doxycycline, while 50 received a placebo. The main result was the rate of progress from baseline to 12 weeks as measured by a composite indicator of ocular motility (increase of ≥ 8°), eyelid aperture (reduction of ≥ 2 mm), proptosis (reduction of ≥ 2 mm), and Graves ophthalmopathy-specific quality-of-life (GO-QOL) scale score (increase of 6 points). Unfavorable events were noted.
Key results of the trial:
- In the intention-to-treat population, the improvement rate at week 12 was 22.0%; 95% CI, 5.0-39.0; P =.01 in the doxycycline group and 16.0% (8 of 50) in the placebo group.
- Similar findings were obtained from the per-protocol sensitivity analysis (39.6% [19 of 48] vs 16.0% [8 of 50]; difference, 23.6%; 95% CI, 6.4-40.8; P =.009).
- Other than one episode of moderate gastric acid regurgitation, neither group experienced any negative effects.
The data support the use of doxycycline for moderate TAO, but caution should be exercised given the cohort size and very little follow-up, concluded the authors.
REFERENCE
Pan Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, et al. Doxycycline vs Placebo at 12 Weeks in Patients With Mild Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online September 29, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.3779
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


