- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pentosan polysulfate sodium use related to retinal disorders: JAMA
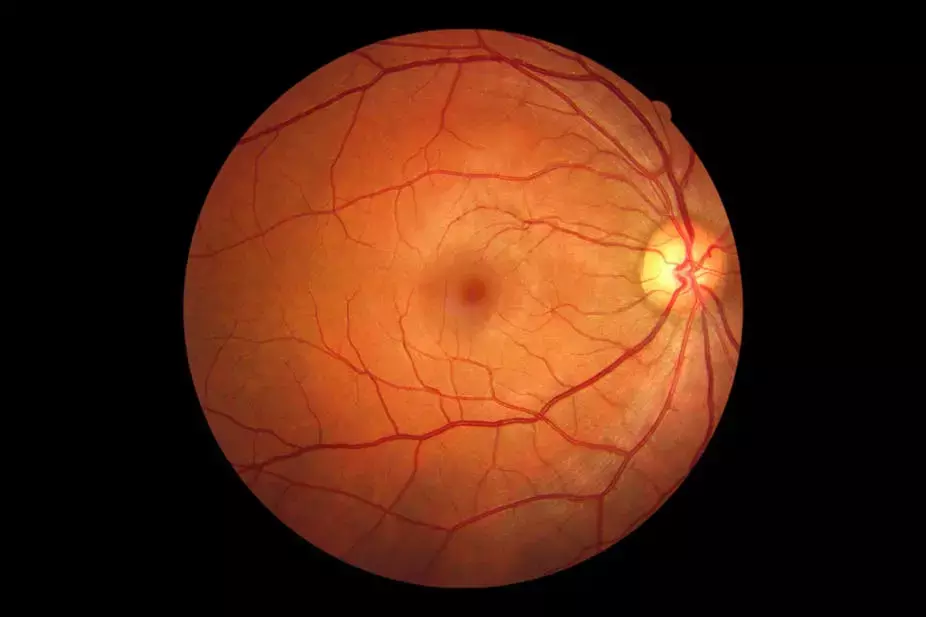
Birmingham: A recent study published in the journal JAMA Ophthalmology has revealed an association between the use of pentosan polysulfate sodium (PPS) and an elevated risk of maculopathy.
Case series have suggested a link between PPS usage and a macular condition. However, observational studies seeking to quantify this association have given equivocal results. To clarify the same, Gerald McGwin Jr, the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, and colleagues aimed to estimate the association between PPS exposure and maculopathy.
From January 2013 to June 2020, this disproportionality research was carried out utilizing the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Adverse event records for pentosan polysulfate were chosen and compared to adverse event reports for medicines used to treat interstitial cystitis, cystitis, bladder problem, or bladder discomfort.
The retinal disorders Standardized Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) Query was used to identify retinal adverse events, which include conditions associated with retinal damage caused by a blockage of its blood supply, nutritional deficiencies, toxins, and diseases affecting the retina.
According to the findings of this study, PPS users are more likely to report adverse events for retinal problems in general than users of other bladder pain drugs. Adverse events for particular macular (eg, macular degeneration, maculopathy) and retinal (eg, retinal toxicity, retinal damage) conditions were more prevalent in individuals who used PPS, although visual function adverse events such as blurred vision and lower visual acuity were less common.
In conclusion, this study adds to the variety of study approaches utilized to investigate the link between PPS and macular degeneration. Although individual observational studies cannot demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships, a growing amount of epidemiologic, clinical, and pathophysiologic data supports the notion that PPS usage may result in maculopathy.
Reference:
McGwin G, MacLennan P, Owsley C. Association Between Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium and Retinal Disorders. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online November 18, 2021. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.4778
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


