- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study finds cyclosporine A gel effective against dry eye disease
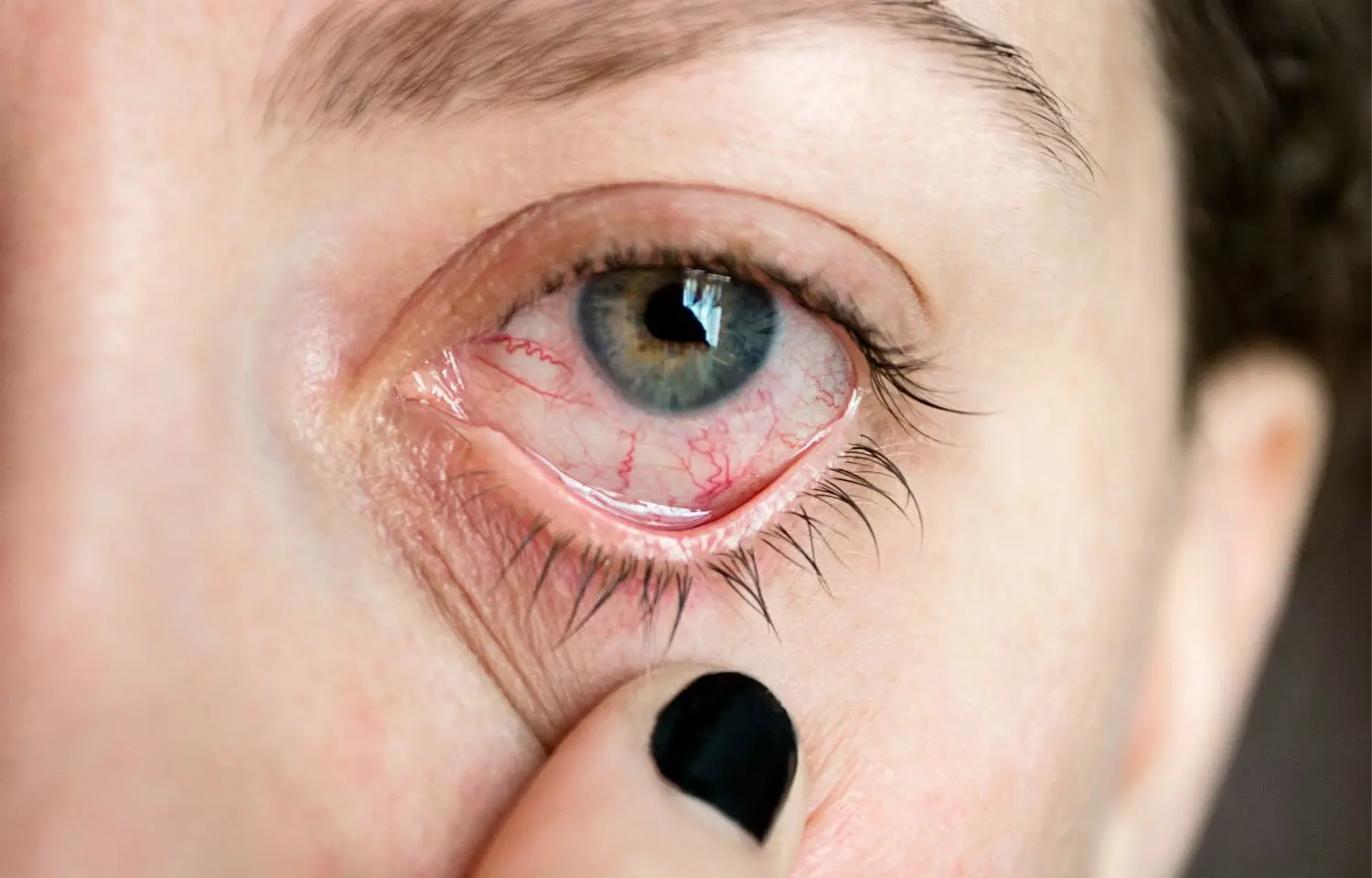
China: A new study published in Drug Design, Development and Therapy Journal shows that participants treated with cyclosporine A gel (CyclAGel, 0.05% CsA) QD for moderate-to-severe dry eye disease (DED) clinically improved and had better statistics in inferior corneal staining score (ICSS), tear production, and symptoms.
Dry eye disease is a multifactorial ocular surface illness characterized by a lack of tear film equilibrium and accompanied by ocular symptoms. DED is caused by tear film instability and hyperosmolarity, ocular surface inflammation and injury, and neurosensory abnormalities. Cyclosporine A (CsA) is a selective immunomodulator that reduces T-cell activation and T-lymphocyte infiltration of the lacrimal glands, inhibits ocular surface epithelial cell death, and is useful in the treatment of DED. This study was carried out by Wenyan Peng and colleagues in order to confirm the effectiveness and safety of a new ophthalmic CyclAGel, 0.05% in treating patients with moderate-to-severe dry eye conditions.
The COSMO study was a multicenter, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled phase III experiment. Between November 2020 and April 2021, patients with moderate-to-severe DED were enrolled at 37 hospitals in China. Eligible participants were randomly assigned to receive either CyclAGel 0.05% or vehicle eye drops once a night (QD). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who improved by at least one point on the ICSS at day 84. TEAEs (treatment-emergent adverse events) were documented.
The key findings of this study were:
1. The CyclAGel and vehicle groups each had 315 and 312 individuals in the full analysis set (FAS). The main efficacy endpoint was met.
2. The proportion of participants having at least a 1-point improvement in ICSS from baseline to day 84 in the CyclAGel group was substantially greater than in the vehicle group.
3. Significant improvements in the ICSS and Oxford scale grading of corneal and conjunctival fluorescein staining were also found at days 14, 42, and 84 when compared to the vehicle.
4. On days 14 and 84, the Schirmer tear test findings were considerably greater in the CyclAGel group than in the vehicle group.
5. The TEAEs were largely modest, and the CyclAGel 0.05% was well tolerated. Eye discomfort was the most common treatment-related TEAE.
In conclusion, in moderate-to-severe DED, CyclAGel 0.05% QD significantly decreased corneal and conjunctival staining and enhanced tear secretion compared to the control group. It also greatly reduced the symptoms. CyclAGel 0.05% QD is a new effective, safe, and well-tolerated therapy alternative for moderate-to-severe DED that may provide additional benefits of convenience and compliance as a once-a-day treatment.
Reference:
Peng, W., Jiang, X., Zhu, L., Li, X., Zhou, Q., Jie, Y., You, Z., Wu, M., Jin, X., Li, X., & Zhou, S. (2022). Cyclosporine A (0.05%) Ophthalmic Gel in the Treatment of Dry Eye Disease: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Masked, Phase III, COSMO Trial. In Drug Design, Development and Therapy: Vol. Volume 16 (pp. 3183–3194). Informa UK Limited. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.s370559
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


