- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Thyroid eye disease patients report maintained improvement 2 years after teprotumumab infusions, reveals research
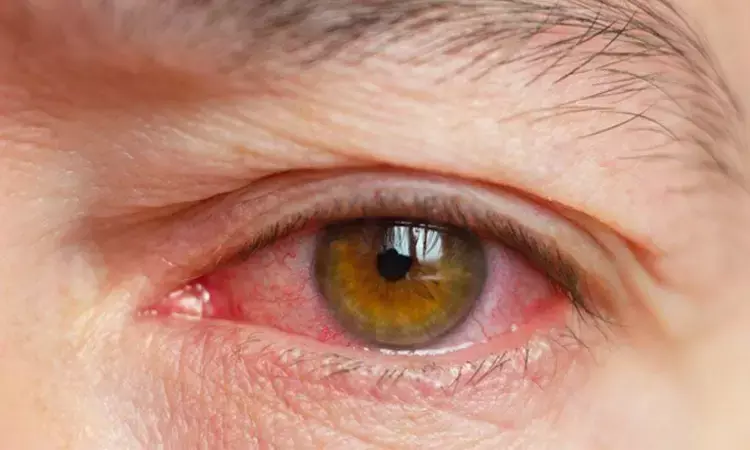
Most patients with thyroid eye disease treated with teprotumumab didn't require additional treatments nearly 2 years later, according to industry-supported research being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass., and published in the journal Thyroid.
“Thyroid eye disease is a lifelong autoimmune disease that can worsen or flare, regardless of how it has been treated. This is the case for many autoimmune diseases,” said George Kahaly, M.D., Ph.D., professor of medicine and endocrinology at Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center in Mainz, Germany. “Given the enduring nature of thyroid eye disease, it is important to understand whether patients who are treated with a full course of teprotumumab (eight infusions) can expect to experience lasting improvements in signs and symptoms, like eye bulging and double vision.”
Due to the longevity of thyroid eye disease, Kahaly added, it was important to look at longer-term results after treating patients with teprotumumab. Kahaly and colleagues sought to answer whether or not patients with thyroid eye disease would see sustained improvements in eye bulging (proptosis) and double vision (diplopia).
The study was sponsored by Amgen, which manufactures teprotumumab.
The researchers analyzed pooled clinical trial data beyond the 24-week treatment period for patients in phase 2, OPTIC, and OPTIC-X studies who received a full course of teprotumumab, up to week 72 (51 weeks post-final teprotumumab infusion). They also investigated whether or not patients received additional therapy from week 24 through week 120 (99 weeks post-therapy) as a measure of persistent benefit.
The data revealed patients who received teprotumumab mostly maintained efficacy 51 weeks after the final infusion at week 72.
Nearly two years after the treatment period was complete, 82% of patients did not need further treatment for thyroid eye disease. Of the 106 reporting patients, 18% (19/106) received additional medication, either systemic steroids or teprotumumab, and/or remedial periocular surgery as of 99 weeks post-therapy.
“As physicians consider treatment approaches for their thyroid eye disease patients, they now have longer-term data to support the use of teprotumumab in appropriate patients,” Kahaly said.
Reference:
Thyroid eye disease patients report maintained improvement 2 years after teprotumumab infusions, The Endocrine Society, Meeting: ENDO 2024.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


