- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical ophthalmic antibiotics not tied with increased adverse neonatal outcomes: Study
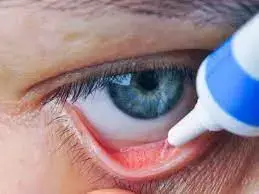
Treatment of chalazia, hordeola, blepharitis, and bacterial conjunctivitis with topical ophthalmic antibiotics does not increase the risk of adverse neonatal outcomes despite the lack of first-pass metabolism with the use of topical medications according to a recent study published in the Eye.
A study was conducted investigating the association between exposure to topical ophthalmic antibiotics during pregnancy and adverse neonatal outcomes.
In this retrospective cohort study, we identified pregnant women with hordeola, chalazia, blepharitis, or bacterial conjunctivitis from 2005 to 2018 using the Japanese Medical Data Centre Claims Database. From the eligible women, we extracted women who have dispensed no topical antibiotics during the first trimester (non-antibiotic group), women who have dispensed topical fluoroquinolones alone at least once (fluoroquinolone alone group), and women who have dispensed any single type of antibiotic (single-antibiotic group). We compared the frequency of congenital anomalies (CA), preterm birth (PB), low birth weight (LBW), and the composite outcome of these three between the fluoroquinolone and non-antibiotic groups and between the single-antibiotic and non-antibiotic groups, using propensity score adjustment.
Results:
- A total of 891 eligible women were identified. In the fluoroquinolone (n = 409) and non-antibiotic (n = 309) groups, CA occurred in 6.8% and 6.8%, PB in 2.4% and 3.2%, LBW in 2.9% and 3.2%, and the composite outcome in 10.5% and 11.3%, respectively.
- Analysis using propensity score adjustment showed no significant difference between the groups in the frequency of CA, LBW, or the composite outcome.
- A comparison of the single-antibiotic and non-antibiotic groups showed similar results.
Thus, topical ophthalmic antibiotics for hordeola, chalazia, blepharitis or bacterial conjunctivitis during the first trimester were not associated with increased adverse neonatal outcomes.
Reference:
Safety of topical ophthalmic antibiotics in pregnant women with hordeola, chalazia, blepharitis, or bacterial conjunctivitis: a propensity score analyses by Yohei Hashimoto et al. published in the Eye.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-021-01586-y
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


