- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Vitamin D deficiency linked to worse symptoms in dry eye patients, finds study
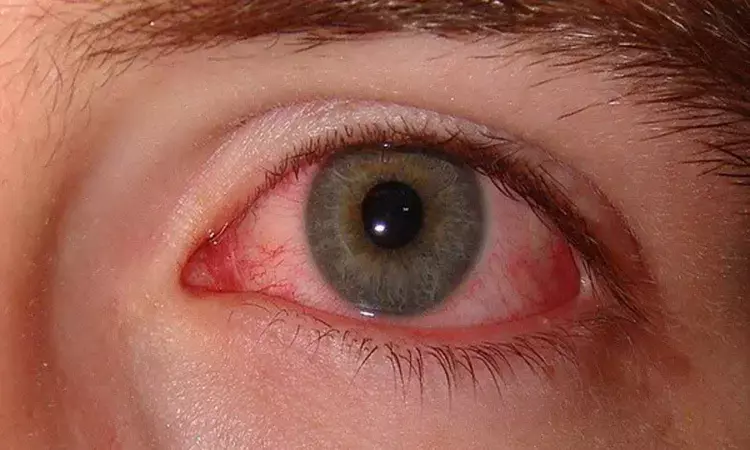
China: Dry eye patients having vitamin D deficiency may experience less tear production and worse subjective symptoms, according to a recent study published in the journal Acta Ophthalmologica. This suggests that vitamin D deficiency might be a risk factor for dry eye syndrome.
Jing Liu, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China, and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta‐analysis to determine the association between vitamin D level and dry eye.
The researchers performed a systematic literature search using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases. The studies that evaluated the association between vitamin D and dry eye were included. The random‐effect model was used to combine the results. Overall, a total of 10 studies consisting of 18919 patients were included.
Read Also: Vitamin D intake may decreases risk of stroke finds study
Key findings of the study include:
- Patients with dry eye had a mean serum vitamin D level that was lower than that in healthy controls by 3.99 ng/ml.
- The mean Ocular Surface Disease Index score was higher (mean difference 10.70) and Schirmer's test without anesthesia result was lower (mean difference 6.38 mm/5 min) in patients with vitamin D deficiency than in controls.
- Tear break‐up time was comparable in the vitamin D deficiency and control groups.
- Sensitivity analyses indicated that the results obtained were robust.
"This meta‐analysis suggested that vitamin D deficiency is associated with worse subjective symptoms and less tear production in patients with dry eye. Vitamin D deficiency may be a risk factor for dry eye syndrome," wrote the authors.
"Prospective cohort and intervention studies are warranted to determine if vitamin D has a protective role in the development of dry eye," they concluded.
Read Also: PCOS patients at higher risk of developing dry eye
The study, "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with dry eye syndrome: a systematic review and meta‐analysis," was published in the journal Acta Ophthalmologica.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


