- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Cilostazol addition may prevent restenosis of carotid arteries after stenting
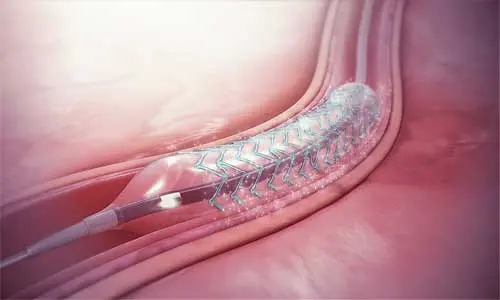
LOS ANGELES -Blockage of the carotid artery is a major cause of stroke. Opening the carotid artery with a mesh tube known as a stent is an effective treatment, however, patients can develop a blockage - known as in-stent restenosis, which may increase the risk of recurrent stroke.
Researchers have found that adding cilostazol - an antiplatelet medication used to treat peripheral vascular disease - tended to prevent re-blockage of carotid artery stents within two years. The study was presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2020.
Cilostazol is a unique antiplatelet agent. As a phosphodiesterase III inhibitor, it improves endothelial function, inhibits the clumping of blood cells (platelet aggravation), widens blood vessels (vasodilator) and mildly inhibits cell growth. It is FDA-approved to treat leg pain in people with peripheral vascular disease.
"This is the first trial to show the potential effectiveness of medical management for the prevention of in-stent restenosis after carotid artery stenting," said Hiroshi Yamagami, M.D., Ph.D., lead study author and director of the Department of Stroke Neurology at National Hospital Organization Osaka National Hospital, Japan.
The Carotid Artery Stenting with Cilostazol Addition for Restenosis (CAS-CARE) study is a multi-centre, prospective, randomized, open-label trial evaluating the inhibitory effect of cilostazol on in-stent restenosis, compared to other antiplatelet medications in patients scheduled to undergo carotid artery stenting.
Eligible patients were randomly assigned to receive cilostazol (50 mg or 100 mg, twice per day), or any antiplatelet agents other than cilostazol, starting three days before stenting and continued for two years. A total of 631 patients (average age 70, 88% of men) were included in the full study analysis. In-stent restenosis occurred in 9.5% of patients in the cilostazol group and 15% of patients in the non-cilostazol group during two years of follow-up. The rate of cardiovascular event occurrence was about 6% in both groups. Bleeding events were also similar for both groups at 1.1% in those treated with cilostazol vs. 0.3% among those not treated with cilostazol.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


