- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
All JAK inhibitors found effective for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in real life setting
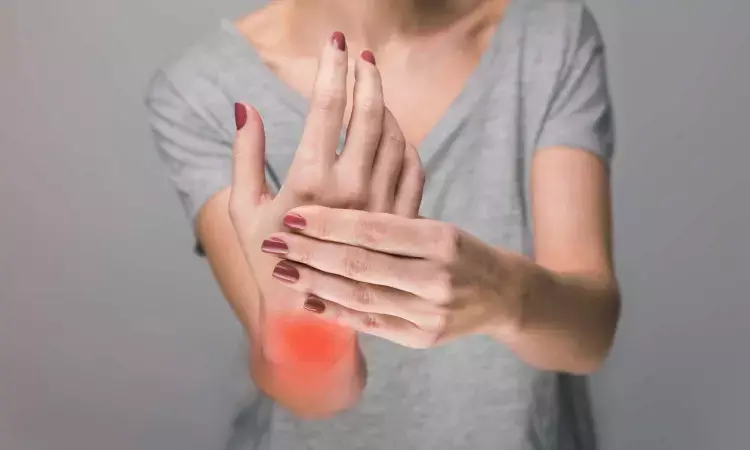
According to a new paper in Rheumatology, published by Oxford University Press, JAK inhibitors, which doctors have used to treat patients with arthritis despite concerns about the effectiveness of such drugs, actually do work quite well. In a multicenter, retrospective study Japanese researchers found that the drugs resulted in impressive remission rates in patients, most of whom choose to continue such treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation of joint linings and results in progressive joint destruction and other systemic complications. The use of biological disease-modifying drugs enables patients to enjoy the achievement of low disease activity and remission. But clinics must administer such drugs through subcutaneous or intravenous routes, which is unpleasant for patients, and over time these drugs commonly become less effective.
Recently scientists have developed Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for arthritis treatment. Patients take such drugs orally. Previous research has demonstrated the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in randomized controlled trials. However, some researchers have questioned the potential efficacy of JAK inhibitors for widespread patient use. In practice, doctors mostly treat patients with JAK inhibitors precisely because those patients have other health problems and so conventional drugs like methotrexate are less effective on them. Real-world patients have distinctive characteristics compared with the patients recruited in randomized controlled trials.
In the present multicenter, retrospective study, researchers using data from 622 patients treated at seven major university hospitals in Japan compared the efficacy and safety of four common JAK inhibitors: tofacitinib, baricitinib, peficitinib, and upadacitinib.
The researchers here found that approximately one in three patients reached remission, three in four reached at least low disease activity, with both numbers representing impressive efficacy. They noted that more than 80% of the patients were still on the JAK inhibitor drugs after six months.
They believe that this is particularly relevant given that immunological secondary treatment failure, where drugs cease to be effective because they produce adverse immune system responses in patients, cannot occur with these oral medications. Immunological secondary treatment failure is common in patients who treat their arthritis with drugs like methotrexate.
Reference:
Shinya Hayashi, Koichi Murata,Real-world comparative study of the efficacy of Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the ANSWER cohort study, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kead543
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


